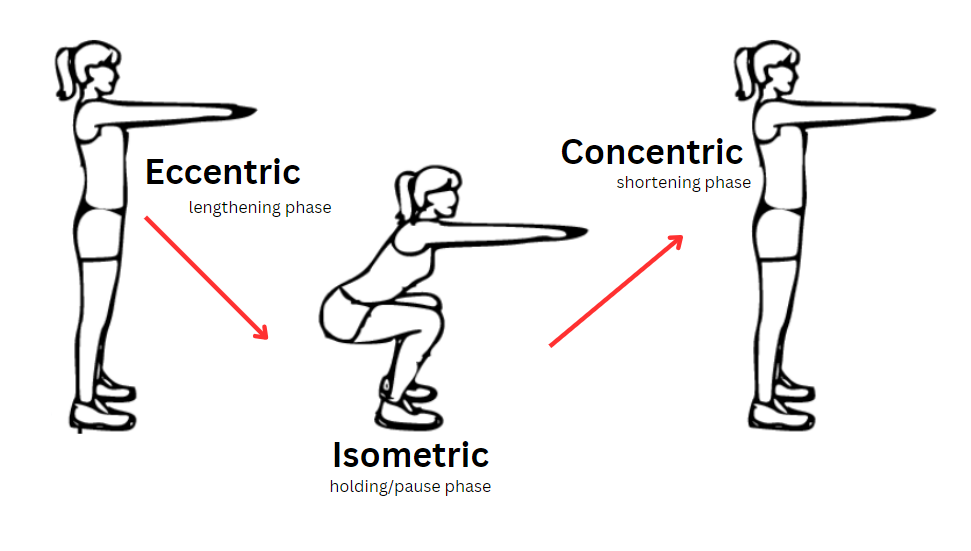
Eccentric Training: Building Strength and Muscle with Controlled Movements
Eccentric training, or negative training, is a specialized exercise technique that focuses on the muscle-lengthening phase of an exercise. This type of training places emphasis on the “eccentric” portion of a movement, which occurs when the muscle is lengthening under load. For example, in a bicep curl, the eccentric phase is the downward motion as you lower the weight. Eccentric training has gained popularity because of its unique effectiveness in promoting muscle growth, improving strength, and enhancing flexibility. This article explores why eccentric training works so well, its impact on muscle stretching, and the role of muscle tearing for hypertrophy.
Thank you for taking the time to read my article! I spend countless hours researching the best techniques that I wish I knew about sooner to provide for anyone to learn about. I hope you learn something useful 😉
What Makes Eccentric Training Effective?
Eccentric training is particularly effective because it capitalizes on the muscle’s ability to handle more load during the lengthening phase than the shortening (concentric) phase. Research indicates that muscles are about 1.3 to 1.75 times stronger eccentrically than concentrically, meaning they can resist higher loads as they lengthen. This higher load capacity leads to greater muscle fiber recruitment, resulting in more substantial adaptations, such as muscle growth and increased strength.
This means eccentric reps are able to be worked harder
You can workout harder by ending your set with assisted negative reps after you can no longer perform a rep with proper form. This will allow for much more muscle growth!
Additionally, eccentric movements require the muscle to work in a controlled manner, which increases time under tension (TUT). Longer TUT is directly correlated with muscle hypertrophy since it forces the muscle fibers to remain engaged, leading to increased metabolic stress and microtears that are crucial for muscle growth.
The Role of Muscle Stretching and Flexibility
Eccentric training is unique in that it naturally incorporates a stretch under tension, which can improve flexibility over time. When a muscle is lengthened under load, it experiences greater elongation than it would with a simple passive stretch. This is known as “loaded stretching”, which enhances the muscle’s pliability and increases its range of motion. Over time, this can lead to improved flexibility and reduced injury risk.
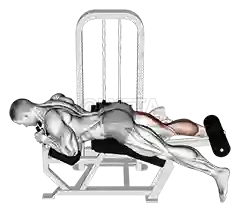
For example, during an eccentric hamstring curl, the muscle elongates as you lower the weight slowly, stretching the fibers and connective tissues. This “active stretch” is more effective than static stretching because it targets both muscle tissue and the surrounding fascia (connective tissue), promoting long-term flexibility gains that are functional and dynamic.
The Importance of Muscle Tearing in Eccentric Training
One of the most critical aspects of muscle growth, or hypertrophy, is muscle tearing. When you perform eccentric training, the controlled lengthening of the muscle under heavy load causes small microtears in the muscle fibers. These microtears are a normal and essential part of muscle adaptation; they signal the body to repair the damaged fibers, making them thicker and stronger in the process.
Eccentric training tends to cause more muscle damage than concentric or isometric training, which is why it is often followed by muscle soreness, known as delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS). This increased muscle tearing during the eccentric phase is beneficial for hypertrophy, as the repair process not only strengthens the muscle but also increases muscle size over time.
How to Incorporate Eccentric Training into Your Workout
To maximize the benefits of eccentric training, it’s best to integrate it into your workout thoughtfully:
Slow Down the Negative Phase: Take 3-5 seconds to lower the weight during exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses. The slower tempo increases time under tension and allows for better muscle engagement.
Use Heavier Weights on Eccentric-Only Exercises: For more advanced lifters, using a heavier weight during the eccentric portion can help push muscle adaptation further. For instance, use a spotter to assist you in lifting the weight (concentric phase), then control the descent on your own.
Focus on Compound Movements: Incorporate eccentric emphasis on compound movements like squats, pull-ups, and presses. These exercises engage multiple muscle groups and allow you to place more load on the muscles during the eccentric phase, enhancing overall strength and hypertrophy.
Allow Adequate Recovery: Due to the increased muscle damage associated with eccentric training, it’s essential to allow for recovery. Make sure to incorporate rest days and avoid overloading the same muscle group in consecutive sessions.
Benefits of Eccentric Training
Enhanced Muscle Growth
Improved Strength
Increased Flexibility and Range of Motion
Greater Neuromuscular Control
What to Do Next: Progressing with Eccentric Training
To continue benefiting from eccentric training:
Gradually Increase Weight: Start with manageable weights, and as you become comfortable, increase the load during the eccentric phase.
Vary Tempo: Changing the speed of the eccentric phase, such as increasing to a 6-second descent, can provide a new challenge for the muscles and promote further adaptation.
Monitor Recovery: Eccentric training can be taxing, so be mindful of soreness levels and ensure your recovery includes proper nutrition and hydration.
Combine with Other Training Styles: Integrate eccentric training with traditional hypertrophy or strength training phases to create a well-rounded program.
Eccentric training is a powerful approach for anyone looking to build muscle, increase strength, and improve flexibility. By emphasizing the lengthening phase, it provides unique advantages that go beyond standard concentric-focused workouts. Incorporating eccentric movements not only challenges your muscles to grow through increased microtearing and time under tension, but it also enhances flexibility and neuromuscular control. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned lifter, adding eccentric training into your routine can be transformative for long-term strength and fitness progress.
This technique, paired with adequate recovery and consistent training, can lead to significant gains in muscle size, strength, and overall athletic performance.
Thanks For Reading!



