Ultimate Leg Workout Guide: Build Stronger Quads, Hamstrings, Glutes, and Calves
Have you ever seen bodybuilders with massive upper bodies and tiny legs? I know you have! Don’t be like that. If you have any interest in a athletic sport, or even interest in your own body composition this page is for you. You HAVE to keep working your legs..
Why Training Your Legs Is So Important
Leg training is essential for anyone serious about bodybuilding and overall muscle development. Your legs consist of some of the largest and most powerful muscles in the body, which play a crucial role in almost every physical activity—from lifting and running to balance and stability. Skipping leg day or underestimating its importance is one of the most common mistakes made by many athletes and lifters. Not only does proper leg training help build strong and massive legs, but it also triggers an increase in key hormones like testosterone and human growth hormone (HGH), which contribute to overall muscle growth and fat loss.
Focusing on leg training also promotes symmetry and balance in your physique. A well-developed upper body paired with undertrained legs leads to an imbalanced and disproportionate look, something every serious bodybuilder wants to avoid. The challenge of leg workouts—whether it’s the intensity of squats or the burn of lunges—builds both mental and physical toughness.
Success in leg training comes down to pushing through discomfort and focusing on consistency and form, setting the foundation for both strength and hypertrophy in every muscle group.
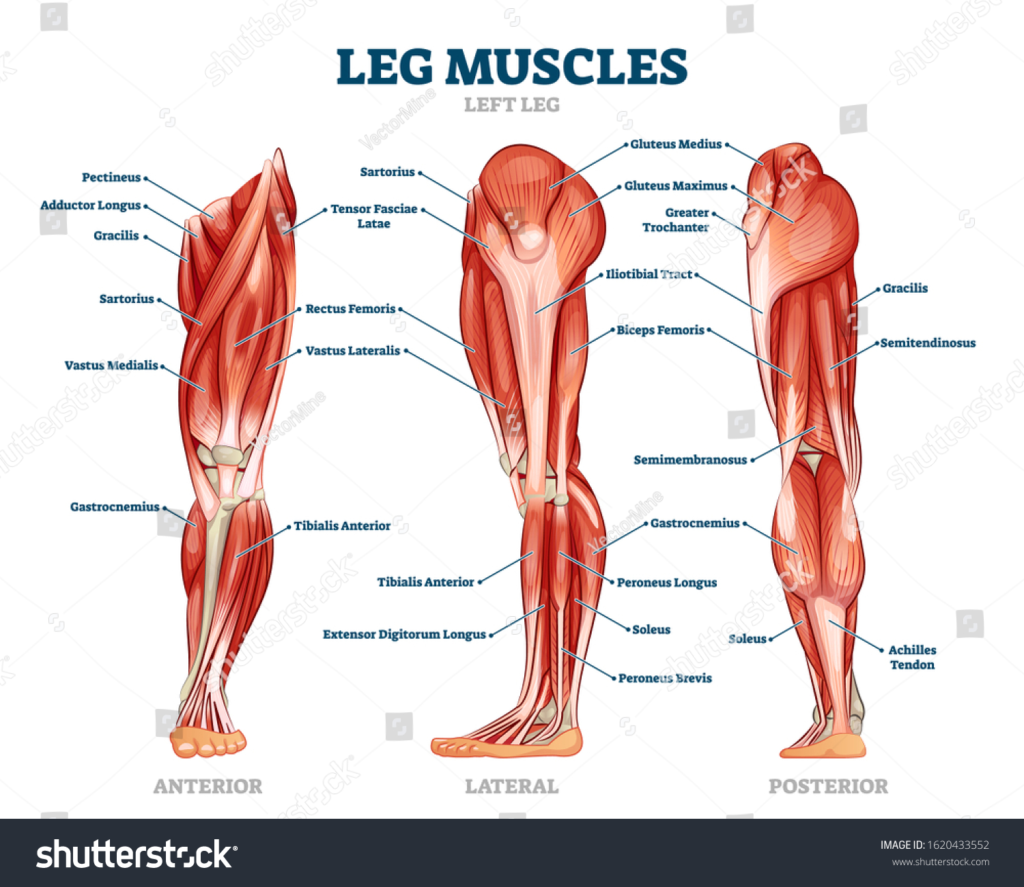
Your legs are made up of some of the largest muscles in your body, playing a huge role in movement, stability, lifting, and overall functionality. Working out your legs won’t only strengthen and grow your legs, but it also produces cortisol, testosterone, and human growth hormone (HGH).
Having proper form and technique is crucial, especially when working out the lower body. If you haven’t already warmed up, and you are using improper technique, you put yourself in a disaster that’s bound to have more consequences than good. When doing squats for example, your entire body should be warmed up and stretched out. The bar should lay on top of your upper back, traps, and shoulders, and when you go down, you control the weight and your legs become parallel to the floor or deeper. Then, keeping your heels on the ground rooted in place, push as hard as you can from the bottom position to come up and restart. It’s simple when you think about it but in reality, it’s a difficult and painful exercise everybody who lifts weights needs to be doing!
Training Your Legs To be Strong
When training for large muscles its good to know how to isolate those muscles. Here are the different muscles you will need to isolate!
Quadriceps
To develop strong quadriceps you there are 4 essential exercises, squats, lunges, leg press, and leg extensions. Obviously there are a billion other things you can do that just might work for you, but as for the basic essential exercises those are it!
Hamstrings
Developing stronger hamstrings are easy! The biggest tip is to go SLOW!! Not in all cases but most of them, stretch induced hypertrophy is what you’re looking for when training hamstrings. The exercises you’ll find yourself doing when training hamstrings tend to be Romanian deadlifts, hamstring curls, and reverse hyperextensions.
Adductors
The adductors are important not only for preventing injury but they also improve leg stability, and flexibility! Some easy exercises you can do to strengthen your adductors are side -lying leg lifts, the adductor machine, sumo squats, and lateral lunges. Remember when training the adductors at all, it’s good to stretch to prevent yourself from an injury.
Glutes
The “glutes” or gluteal muscles are essential for hip movement, and mobility. they also support the lower back when lifting, they help prevent knee injury, and finally training your glutes also improves posture! Some exercises that work the glutes are lunges, RDL’s, donkey kicks, glute bridges, hip thrusts and bulgarian split squats.
Tibialis Anterior
The Tibialis Anterior, is real easy to train! It plays a major role in lifting the foot upwards, and maintaining balance while walking or running. Strengthening the tibialis anterior can help improve athletic performance, prevent shin splints, and contribute to overall lower leg stability. Some great exercises to train the tibialis are tibialis raises with or without weight, resistance band toe flexion, jump rope, and box jumps.
Calf muscles
Calves are like the back bone to your legs. Without proper calf training, your legs will look insignificant to the rest of your body. Training calves also helps reduce soreness, prevents shin splints, and increases stability. Some of the best exercises to target the calves are calf raises with or without weight, box jumps, running and jump rope.
The Importance Of Leg Strength


Building leg strength enhances your ability to lift heavier weights across the board. Exercises like squats and deadlifts not only improve leg strength but also generate power for upper body lifts...
Training large muscle groups like the quads, hamstrings, and glutes stimulates a significant hormonal response. Exercises that target these muscles promote the release of growth hormones...
Strong legs create a more stable foundation for the rest of the body. Weak or underdeveloped leg muscles can lead to poor movement patterns and imbalances that increase the risk of injury...

A well-proportioned physique is key to bodybuilding success, and leg development is a critical component of that symmetry. Many bodybuilders make the mistake of focusing too much on upper body muscles...
Leg strength is the foundation of a powerful and balanced physique. Strong legs aren’t just crucial for lower body aesthetics, but they also play a major role in overall performance, stability, and longevity in bodybuilding.

Beyond bodybuilding, leg strength translates into improved performance in daily activities. Simple movements like walking, running, and standing for long periods are made easier by strong leg muscles...
The Leg Day Mentality: Train Hard, Train Smart
The mentality needed for leg training is one of grit, determination, and consistency. Leg workouts are often considered the most physically and mentally challenging in bodybuilding, but they are essential for overall muscle development, athletic performance, and functional strength.

Success in leg training hinges on overcoming mental blocks, maintaining patience and consistency, and committing to proper form. As you face the physical challenges of leg day, the mental barriers can be daunting, often tempting you to skip reps or settle for less than your best. Embracing the discomfort while staying patient allows you to push through these hurdles and build strength over time. Consistent effort, paired with a commitment to executing each movement with precision, not only enhances your performance but also fosters a mindset of resilience. By focusing on technique and prioritizing proper form, you cultivate a foundation of strength that translates into long-term gains, reinforcing the belief that progress is achieved through dedication and unwavering focus.

Leg day is notorious for being uncomfortable. Whether it’s the burn during squats or the fatigue from deadlifts, you’ll have to mentally prepare to push through the discomfort. The pain is often a sign that your muscles are working hard and breaking down to grow back stronger. Successful athletes learn to thrive on this feeling, knowing that this struggle is what leads to progress.
The mind-muscle connection plays a huge role in leg training. This means being mentally present during every lift, focusing on engaging the right muscles, and ensuring your technique is perfect. Rather than going through the motions, you'll need to visualize each muscle working as you perform exercises like squats, leg presses, and lunges. This kind of mental focus amplifies your training results.
Important Leg Exercises
Squats
Squats are a fundamental compound exercise that targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. They promote overall leg strength and stability, making them essential for any leg training program. Variations include back squats, front squats, and goblet squats, each emphasizing different muscle groups.
How to Do It: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and your toes slightly pointed outward. Keep your chest up and your back straight. Lower your body by bending at the hips and knees, keeping your weight on your heels. Go down until your thighs are at least parallel to the ground. Push through your heels to return to the starting position. Variations include:
- Back Squats: Barbell on your upper back.
- Front Squats: Barbell across your front shoulders.
- Goblet Squats: Holding a dumbbell or kettlebell at chest level.


Deadlifts
Deadlifts primarily work the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back. They are critical for developing posterior chain strength, which is vital for athletic performance and functional movements. Variations such as sumo deadlifts and Romanian deadlifts can target specific areas within the legs and hips.
How to Do It: Stand with your feet hip-width apart, with the barbell over the middle of your feet. Bend at the hips and knees to grip the bar with both hands, either overhand or mixed grip. Keep your back flat and your chest up as you lift the bar by extending your hips and knees until standing upright. Lower the bar back down by pushing your hips back and bending your knees. Variations include:
- Sumo Deadlifts: Wider stance targeting the inner thighs.
- Romanian Deadlifts: Focus on hip hinge to target the hamstrings.
Lunges
Lunges engage multiple muscle groups in the legs, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. They also improve balance and stability. Forward lunges, reverse lunges, and lateral lunges are effective variations that can add diversity to your leg workout.
How to Do It: Stand upright, then take a step forward with one leg. Lower your body until both knees are bent at about a 90-degree angle. Keep your front knee directly over your ankle. Push through the front heel to return to the starting position. Variations include:
- Forward Lunges: Step forward.
- Reverse Lunges: Step backward.
- Lateral Lunges: Step to the side.


Leg Press
The leg press machine allows for heavy loading of the legs while minimizing strain on the back. It primarily targets the quadriceps but also engages the hamstrings and glutes. Adjusting foot placement can shift the focus between these muscle groups.
How to Do It: Sit on the leg press machine with your back against the pad. Place your feet shoulder-width apart on the platform. Lower the platform by bending your knees until they form a 90-degree angle, keeping your feet flat. Push through your heels to extend your legs back to the starting position. Adjust foot placement to target different muscle groups.
Leg Curls and Extensions
Leg curls isolate the hamstrings, while leg extensions focus on the quadriceps. Both exercises are excellent for building muscle size and strength in the legs. They can be particularly useful for targeting specific muscle imbalances.
How to Do It:
- Leg Curls: Lie face down on the leg curl machine, placing your ankles under the padded lever. Curl your legs up toward your glutes, squeezing your hamstrings at the top. Lower back down with control.
- Leg Extensions: Sit on the leg extension machine with your knees under the pad. Extend your legs straight out in front of you, squeezing your quadriceps at the top. Lower back to the starting position.


Calf Raises
Calf raises target the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles in the calves. They can be performed standing or seated, and incorporating different foot positions can help in developing balanced calf muscles.
How to Do It: Stand with your feet hip-width apart. Lift your heels off the ground, rising onto the balls of your feet. Hold for a moment at the top, then lower your heels back down. This can be done standing, seated, or using a calf raise machine.
Proper Form And Injury Prevention
Maintaining proper form during leg exercises is crucial for maximizing effectiveness and minimizing the risk of injury. Good form ensures that the targeted muscle groups are engaged correctly, allowing for optimal strength gains and muscle development.
Key Principles for Proper Form
Alignment and Posture
Keep your spine neutral and avoid rounding your back. Proper alignment helps distribute weight evenly and prevents undue stress on the spine.
Engage your core to stabilize your body during movements.
Controlled Movements
Perform each exercise in a controlled manner, avoiding rapid or jerky movements. This not only enhances muscle engagement but also reduces the likelihood of injuries.
Joint Positioning
Ensure that your knees track over your toes during squats and lunges to prevent knee injuries. Avoid letting your knees cave inward.
Keep your feet flat and maintain contact with the ground, especially during lifts.
Depth and Range of Motion
Aim for a full range of motion without sacrificing form. For squats, go down to at least parallel, or deeper if flexibility allows, but only if you can maintain proper posture.
Avoid excessive range of motion that can lead to strain or injury, particularly in the lower back or knees.

Breathing Techniques
Use proper breathing techniques to support your movements. Inhale during the lowering phase and exhale during the exertion phase (e.g., when pushing up from a squat).
Injury Prevention Strategies
Warm-Up and Cool Down
Start with Lighter Weights
Listen to Your Body
Always perform a dynamic warm-up before workouts to prepare the muscles and joints. Incorporate movements that mimic the exercises you will perform.
Cool down with static stretching after workouts to improve flexibility and reduce muscle soreness.
Begin with lighter weights to master the form before progressing to heavier loads. Gradually increase the weight as you become more comfortable and confident in your technique.
Pay attention to any pain or discomfort during exercises. If something doesn’t feel right, stop and assess your form or reduce the weight. Pushing through pain can lead to serious injuries.
Use Support and Equipment
Rest and Recovery
Cross-Training
Consider using weightlifting belts, knee sleeves, or proper footwear to provide additional support and stability during lifts.
If unsure about your form, work with a trainer or use mirrors to self-correct
Allow adequate recovery time between leg workouts. Muscles need time to heal and grow stronger, reducing the risk of overuse injuries.
Incorporate a variety of exercises into your routine to prevent muscle imbalances and overuse injuries. Include activities that promote balance, flexibility, and overall strength.
