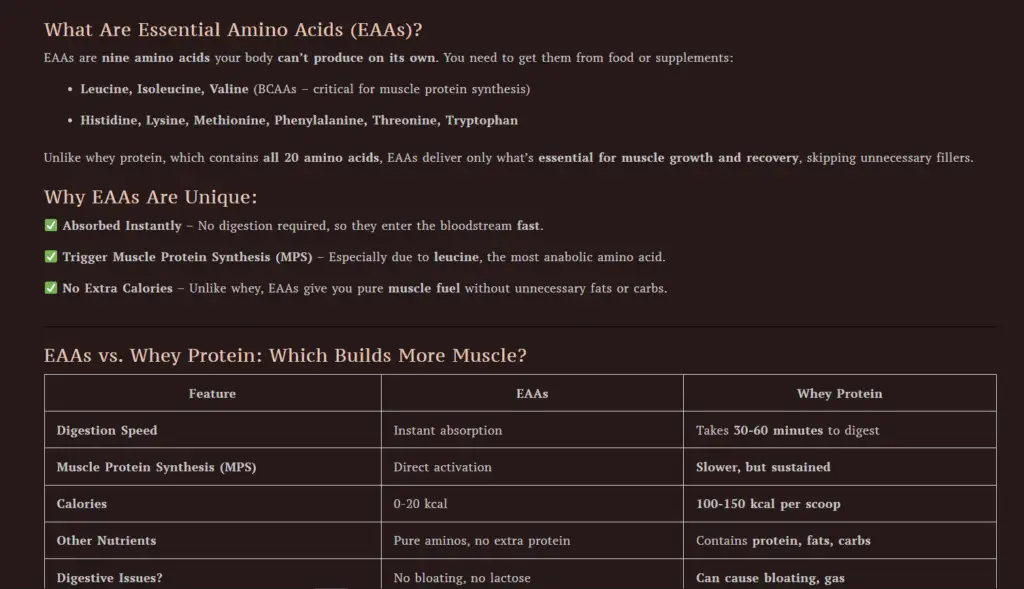
The 7 Benefits of BCAAs: Why They Matter for Muscle Growth and Performance
Want to build muscle faster, recover quicker, and train harder? Studies show that BCAAs may increase muscle growth, reduce soreness and fatigue, prevent muscle wasting, and even support liver health. These essential amino acids—found in foods like meat, eggs, and dairy—are your key to faster recovery, sustained energy, and peak performance. Whether you’re lifting heavy, pushing through endurance workouts, or training fasted, BCAAs can help you unlock 7 powerful benefits that take your results to the next level. Let’s break them down! 💪🔥
🏋️♂️ What Are BCAAs?
Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) are a group of three essential amino acids: leucine, isoleucine, and valine. These amino acids are termed “branched-chain” because of their unique chemical structure, which sets them apart from other amino acids. Unlike most amino acids, BCAAs are primarily metabolized in the muscles, rather than the liver. This makes them an immediate source of energy and a vital player in muscle recovery and growth.
While BCAAs are found in many protein-rich foods, supplementing with them can have targeted benefits, particularly for athletes and fitness enthusiasts looking to optimize their performance and recovery.

1. Boosts Muscle Growth💪
Muscle growth, or muscle hypertrophy, occurs when muscle fibers are subjected to stress during resistance training. This causes tiny tears in the muscle tissue, and as they repair, they grow back stronger and larger. Leucine, one of the three BCAAs, plays a key role in muscle protein synthesis (MPS).
When you consume leucine, it activates a critical protein pathway known as mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin). This pathway signals the muscle cells to begin building proteins that are crucial for muscle growth. In fact, research has shown that leucine supplementation can increase muscle protein synthesis by up to 40%, especially when taken before or after resistance training.
This makes BCAAs particularly effective for enhancing muscle growth when combined with a structured workout routine, especially when consumed at the optimal time around workouts.
Key Takeaway:
Leucine activates mTOR, helping your muscles grow faster and recover better from training.
2. Enhances Workout Endurance🏃️
Isoleucine, another BCAA, plays an important role in supporting energy metabolism during exercise. It helps increase glucose uptake into the muscles, providing them with a ready supply of fuel for sustained activity. This is especially useful in endurance sports or high-repetition strength training.
As an athlete performs long, intense workouts, the body’s glycogen stores (the muscle’s energy reserves) get depleted. Isoleucine helps the muscles use stored fat for energy, which can help spare glycogen, delaying fatigue.
Key Takeaway:
Isoleucine boosts glucose uptake and helps maintain energy levels during prolonged or intense exercise.
3. Reduces Muscle Soreness & Speeds Recovery💪💧
After intense physical activity, your muscles can experience Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS), a condition caused by microtears in muscle fibers. While this is part of the normal recovery process, it can be uncomfortable and hinder your ability to train again quickly.
Research shows that BCAAs, especially when taken before or after a workout, can significantly reduce the severity of DOMS. BCAAs help minimize muscle damage, decrease inflammation, and support the repair process, meaning you can recover faster and get back to your workouts sooner.
Key Takeaway:
BCAAs help reduce muscle damage and soreness, aiding quicker recovery after tough workouts.
4. Prevents Muscle Breakdown (Anti-Catabolic Effects)❄️
Intense exercise, prolonged fasting, or caloric restriction can trigger the body to break down muscle tissue for energy. This is known as catabolism—the opposite of muscle building. By providing a readily available fuel source, BCAAs help prevent this muscle breakdown.
Leucine, isoleucine, and valine serve as fuel for the body during exercise, reducing the need for muscle protein to be broken down into amino acids for energy. This is particularly beneficial when training in a fasted state or during calorie deficits when the body is more prone to catabolism.
5. Fights Fatigue & Improves Mental Focus💀
Valine, the third BCAA, plays an important role in mental focus and fatigue management. During prolonged physical activity, serotonin (a neurotransmitter) levels can rise in the brain, contributing to feelings of fatigue. By competing with tryptophan (the amino acid that boosts serotonin production), valine can reduce the buildup of serotonin, helping to delay fatigue and improve mental clarity.
In practical terms, this means you can stay mentally focused during your workouts, helping you push through tough sessions and finish strong.
Related Articles
6. Supports Fat Loss & Metabolism🌿
While BCAAs are often associated with muscle building, they also have a significant role in fat loss. By supporting the body’s ability to use fat as an energy source, BCAAs can help accelerate fat oxidation, especially when paired with a proper diet and exercise regimen. This is particularly important during calorie deficits, where the goal is to lose fat while preserving lean muscle mass.
Additionally, studies suggest that supplementing with BCAAs can help preserve muscle tissue during fat loss phases, ensuring that the weight lost is predominantly fat.
Key Takeaway:
BCAAs offer a quick, targeted boost for muscle recovery and performance, while whole proteins support long-term muscle repair and growth.
7. Benefit people with liver disease
BCAAs don’t just benefit athletes—they also play a crucial role in liver health. Studies suggest that BCAAs may help people with liver disease, particularly those with cirrhosis, a condition where the liver becomes severely scarred. In individuals with cirrhosis, the liver struggles to process amino acids efficiently, which can lead to muscle loss and other complications.
Research indicates that BCAA supplementation can improve liver function, reduce complications, and even enhance muscle retention in people with liver disease. Additionally, BCAAs may help lower the risk of hepatic encephalopathy, a condition where toxins build up in the brain due to poor liver function, causing confusion and cognitive issues.
While BCAAs are not a cure for liver disease, they can be a helpful dietary support tool for maintaining muscle mass and improving overall liver health when used alongside medical treatment.
⚖️ BCAAs vs. Whole Protein: Which Is Better?
While whole protein sources (such as whey protein or plant-based proteins) contain all the essential amino acids needed for muscle repair and growth, BCAAs offer a more targeted approach. BCAAs are rapidly absorbed and utilized directly by muscles, making them particularly effective around workouts when your body needs quick amino acid delivery.
Whole protein sources are essential for overall muscle recovery and growth over time, but BCAAs can provide an immediate impact during the critical window of muscle repair and recovery immediately following intense exercise.
Best Time to Take BCAAs
- Before Training – To prevent muscle breakdown, enhance endurance, and boost energy levels for better performance.
- During Training – To sustain energy, delay fatigue, and maintain mental focus throughout prolonged exercise.
- After Training – To speed up recovery, reduce soreness, and kickstart muscle protein synthesis.
- Fasted Workouts – To protect lean muscle tissue during training without a food intake.
The Three BCAAs & Their Unique Roles 🏋️♂️
Leucine: The Muscle Growth Trigger 🚀
Primary Role: Stimulates muscle protein synthesis (MPS).
How It Works: Leucine activates the mTOR pathway, a key cellular process that triggers muscle growth. This makes it the most potent of the three BCAAs for building and repairing muscle tissue.
Additional Benefits:
Helps preserve lean muscle mass during calorie deficits.
Enhances recovery after workouts.
Supports glucose uptake and insulin signaling, which can improve energy production.
May reduce muscle soreness and speed up repair by enhancing protein turnover.
Isoleucine: The Endurance Booster & Fat Metabolizer 🔥
Primary Role: Enhances energy production and regulates blood sugar levels.
How It Works: Isoleucine increases glucose uptake and usage by muscle cells, providing a sustained energy source during workouts. It also plays a role in fat metabolism, making it beneficial for endurance athletes and those in cutting phases.
Additional Benefits:
Promotes hemoglobin production (important for oxygen transport).
Supports wound healing and immune function.
May help regulate blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes.
Valine: The Fatigue Fighter & Mental Focus Enhancer 🧠
Primary Role: Reduces fatigue and supports cognitive function.
How It Works: Valine competes with tryptophan (a precursor to serotonin) for transport across the blood-brain barrier. Since serotonin contributes to feelings of fatigue, valine can help delay exhaustion and improve mental clarity during long workouts.
Additional Benefits:
Helps prevent muscle breakdown by acting as an alternative fuel source.
Supports tissue repair and muscle coordination.
May enhance mental performance under stress.
🔎 Final Thoughts
So now you know about the 7 benefits of BCAAs. BCAAs are an essential supplement for anyone serious about improving their physical performance, muscle growth, and recovery. Their scientifically backed benefits make them a game-changer for athletes, bodybuilders, and fitness enthusiasts. By helping with everything from boosting muscle synthesis to reducing soreness and fighting fatigue, BCAAs play a critical role in getting the most out of every workout.
Whether you are aiming to build muscle, recover faster, or improve endurance, incorporating BCAAs into your routine can provide a noticeable impact. And with various sources available—whether in whole foods or supplements—getting the right amount is easier than ever.
👉 Want to know the best sources of BCAAs? [Check out our BCAA-rich foods and supplement guide ➡️]
Thankyou for reading!
Trending Articles:
Do you have any questions?