The Real Reason Protein Is A Power House Nutrient: More Than Just Muscle Fuel
Protein isn’t just for bodybuilders—it’s the foundation of muscle growth, recovery, fat loss, and overall health. This in-depth guide breaks down everything you need to know about protein, from how it fuels muscle protein synthesis (MPS) to its role in hormone regulation, metabolism, and endurance performance. Learn the science behind optimal protein intake, digestion, and absorption, plus the best sources and timing strategies for maximizing results. Whether you’re an athlete, lifter, or just looking to improve your diet, this guide answers every major question about protein—including myths, risks, and hidden benefits most people don’t know.
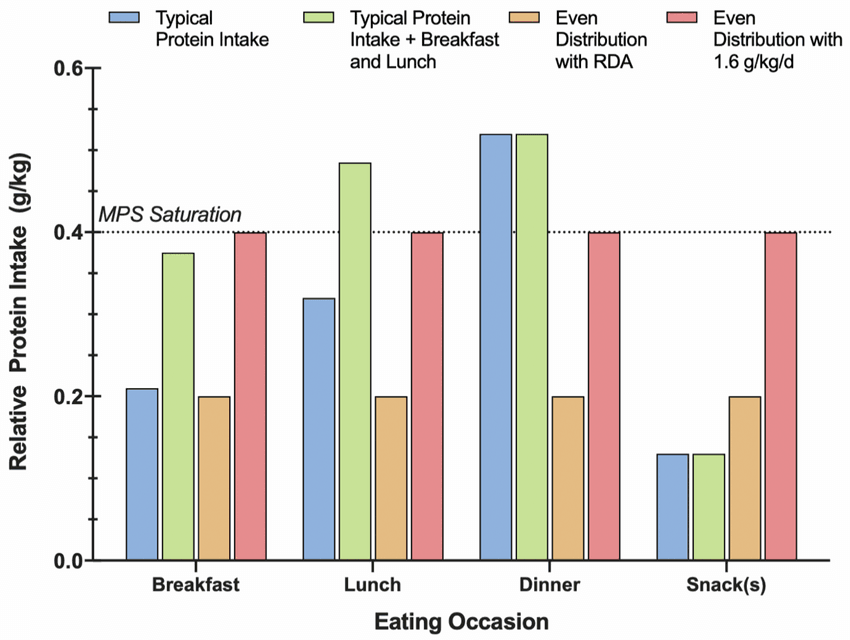
Table of Contents
- What Is Protein?
- Why Is Protein So Important for Muscle Growth?
- Amino Acids: The Building Blocks of Protein
- The Role of Protein in Your Overall Health
- Muscle Protein Synthesis & mTOR Pathway: The Science Behind Protein’s Power
- How Can You Maximize Muscle Protein Synthesis?
- How Much Protein Do You Need?
- How to Time Protein Intake with Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS)
- Protein Quality: Does It Matter?
- The Best Protein Sources: Animal vs. Plant
- When Should You Take Protein?
- How Protein Affects Recovery & Performance
- Protein for Fat Loss: Does It Still Matter?
- Does Protein Help You Lose Weight?
- The Role of Protein in Hormone Regulation
- Does Protein Help Endurance Athletes?
- The Effects Of Too Much Protein
- Protein FAQ
- Key Takeaways
What Is Protein?
Protein is a macronutrient made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of the body. There are 20 different amino acids, 9 of which are essential (must be obtained from food) and 11 of which are non-essential (can be synthesized by the body). Protein is found in every cell of the body and plays a critical role in a variety of biological processes, including muscle growth, repair, immune function, and hormone production.
Why Is Protein So Important for Muscle Growth?
Protein is crucial for muscle repair and growth after physical activity. During exercise, particularly strength training, the muscle fibers undergo stress and small tears. Protein helps repair these tears by providing the body with the necessary amino acids to rebuild stronger muscle tissue. Adequate protein intake helps maximize muscle protein synthesis (MPS), a process responsible for the repair and growth of muscle fibers.
Amino Acids: The Building Blocks of Protein
Amino acids are the compounds that make up protein and are essential for muscle growth, repair, and overall body function. There are 20 amino acids, categorized into three groups:
- Essential Amino Acids – The body can’t produce these, so you must get them from food (e.g., leucine, lysine, valine).
- Non-Essential Amino Acids – Your body can produce these on its own.
- Conditional Amino Acids – Needed in higher amounts during stress, illness, or intense training.
Why Are Amino Acids Important?
✔ Muscle Growth & Recovery – Essential for muscle protein synthesis.
✔ Energy & Performance – Used as fuel when needed.
✔ Hormones & Enzymes – Help regulate metabolism and body functions.
✔ Brain & Mood Support – Some amino acids act as neurotransmitters.
Best Sources of Amino Acids
✅ Complete Proteins (Contain all 9 essential amino acids) – Meat, fish, eggs, dairy, soy, quinoa.
✅ Incomplete Proteins (Lack one or more essential amino acids) – Beans, nuts, grains (combine these to create a complete profile).
Amino acids are vital for muscle and health—make sure your diet includes enough high-quality protein.
What is the Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS)?
PDCAAS is a rating system used to measure protein quality based on:
- Amino acid composition (Does it have all 9 essential amino acids?)
- Digestibility (How well does your body absorb it?)
✅ Best PDCAAS Score (1.0) – Whey, casein, eggs, milk, soy protein.
⚠️ Lower Scores (<1.0) – Most plant proteins (but can be improved by combining sources).
Why It Matters: PDCAAS helps determine how effectively a protein source supports muscle growth and overall health.
The Role of Protein in Your Overall Health
In addition to muscle health, protein is involved in numerous other bodily functions:
- Immune function: Antibodies and immune cells are made of protein.
- Hormone regulation: Protein is involved in the creation of various hormones.
- Enzyme function: Many enzymes, which speed up biochemical reactions in the body, are proteins.
- Transport: Certain proteins transport nutrients (like hemoglobin transporting oxygen in the blood).
- Cell signaling: Protein is involved in the communication between cells.
Are there risks associated with high-protein diets and heart health?
A high-protein diet isn’t necessarily bad for your heart, but the source of protein matters:
✅ Lean proteins (chicken, fish, eggs, plant-based sources) are heart-friendly.
❌ Red & processed meats (bacon, sausage, deli meats) can increase the risk of heart disease due to high saturated fat and cholesterol.
❌ Excess animal protein may also increase homocysteine levels, which is linked to higher heart disease risk.
Bottom Line: High-protein diets are safe if they include lean sources and a balanced intake of healthy fats and fiber.
How Does Cooking Affect the Protein Content in Foods?
Cooking doesn’t destroy protein, but it can change its structure (denaturation), making it easier or harder to digest.
✔ Heat helps – Cooking eggs, meat, and fish can improve digestibility by breaking down tough protein structures.
❌ Too much heat can reduce quality – Overcooking (charring meat, frying at high heat) can damage amino acids and form harmful compounds.
Best Practices: Use moderate cooking methods like grilling, baking, steaming, or boiling to preserve protein quality.
❌ Excess animal protein may also increase homocysteine levels, which is linked to higher heart disease risk.
Bottom Line: High-protein diets are safe if they include lean sources and a balanced intake of healthy fats and fiber.
10 Benefits of Combining Different Protein Sources
Creates a Complete Amino Acid Profile – Some plant proteins lack certain essential amino acids, but combining them ensures you get all nine essential amino acids needed for muscle growth and repair.
Improves Protein Utilization – Your body can better absorb and use protein when you consume a variety of sources instead of relying on just one type.
Enhances Muscle Growth & Recovery – A balanced mix of fast- and slow-digesting proteins provides steady amino acid release, supporting muscle protein synthesis (MPS) over time.
Supports Gut Health – Combining plant-based proteins like legumes and grains increases fiber intake, which boosts digestion and supports a healthy gut microbiome.
Balances Nutrient Intake – Different protein sources provide unique micronutrients (e.g., iron from beans, omega-3s from chia seeds, and B vitamins from eggs), leading to a more well-rounded diet.
Reduces Inflammation – A mix of plant-based proteins lowers reliance on red meat, which may help reduce inflammation and heart disease risk.
Improves Satiety & Fat Loss – Pairing protein with fiber-rich sources (like quinoa or lentils) keeps you full longer, preventing overeating and supporting weight management.
Sustainable & Eco-Friendly – Combining plant proteins (like beans and rice) reduces environmental impact compared to relying heavily on animal-based proteins.
More Cost-Effective – Mixing affordable protein sources (e.g., beans, lentils, rice, and eggs) provides high-quality nutrition without breaking the bank.
Enhances Workout Performance – A mix of fast-acting proteins (whey, eggs) and slow-digesting proteins (casein, legumes) ensures steady energy levels and longer-lasting muscle repair.
Best Protein Combinations for Maximum Benefits
✔ Beans + Rice – A classic complete protein combo with balanced amino acids.
✔ Lentils + Whole Grains (Brown Rice, Quinoa, Oats) – High in protein and fiber, great for muscle growth.
✔ Chia Seeds + Oats – Packed with omega-3s, fiber, and plant protein for energy and satiety.
✔ Hummus + Whole Wheat Pita – A Mediterranean protein-rich snack.
✔ Quinoa + Black Beans – A superfood combo for plant-based protein and essential minerals.
✔ Eggs + Cheese – A fast and slow-digesting protein mix for sustained muscle repair.
✔ Greek Yogurt + Nuts (Almonds, Walnuts, Cashews) – Protein + healthy fats for muscle recovery.
✔ Tofu + Brown Rice – A plant-based meal loaded with protein and muscle-supporting nutrients.
✔ Peanut Butter + Whole Wheat Bread – A budget-friendly protein source with healthy fats.
✔ Edamame + Quinoa – High in protein and fiber, great for vegan muscle-building.
✔ Cottage Cheese + Flaxseeds – High in casein protein, keeping muscles fed overnight.
✔ Chickpeas + Tahini (Hummus) – A well-rounded protein source with healthy fats.
✔ Oatmeal + Almond Butter – Energy-packed with protein, fiber, and slow-digesting carbs.
✔ Spinach + Eggs – A high-protein, iron-rich meal perfect for muscle function.
✔ Tempeh + Avocado – Fermented soy for gut health plus healthy fats for nutrient absorption.
✔ Brown Rice + Hemp Seeds – A complete plant protein with added omega-3s.
✔ Sweet Potatoes + Black Beans – A great high-fiber, muscle-friendly combination.
✔ Fish + Quinoa – Lean animal protein + plant protein for a well-balanced amino acid profile.
✔ Pasta + Peas – Peas boost protein content in pasta dishes.
✔ Seitan + Nut Butter – High-protein plant-based combo with a rich texture.
Muscle Protein Synthesis & mTOR Pathway: The Science Behind Protein’s Power
Muscle growth is fundamentally driven by muscle protein synthesis (MPS)—the process by which your body repairs and builds muscle fibers after exercise. This process is heavily influenced by protein intake and resistance training, and at the core of it all is the mTOR pathway, a key regulator of muscle hypertrophy.
What Is Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS)?
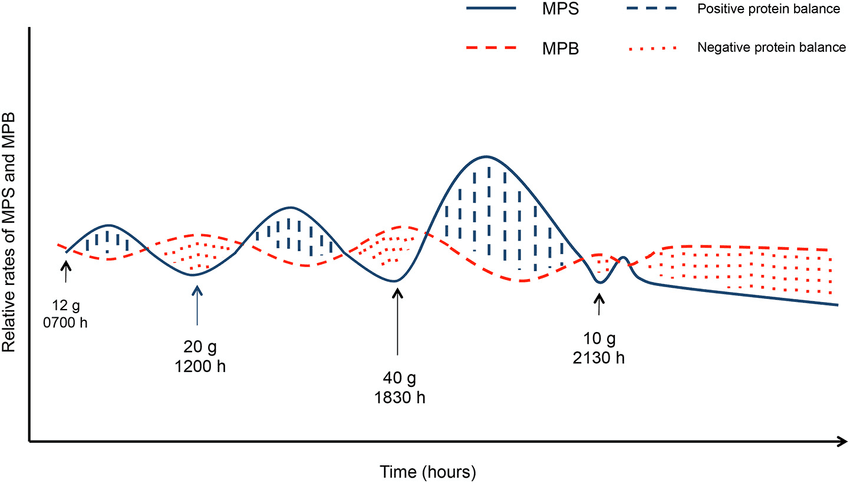
Muscle protein synthesis is the biological process where amino acids from dietary protein are used to repair and build new muscle tissue. MPS occurs continuously throughout the day but spikes after intense exercise or protein consumption.
However, for muscle growth to occur, MPS must exceed muscle protein breakdown (MPB)—the natural degradation of muscle tissue from stress, training, and daily activity. The balance between MPS and MPB determines whether you are gaining, maintaining, or losing muscle mass.
What Triggers Muscle Protein Synthesis?
- Resistance Training – Exercise creates microscopic damage to muscle fibers, which signals the body to repair and strengthen them.
- Protein Intake (Especially Leucine-Rich Foods) – Certain amino acids, particularly leucine, directly stimulate the mTOR pathway, increasing MPS.
- Insulin & Nutrient Availability – Insulin plays a supportive role in MPS by promoting amino acid uptake into muscle cells.
mTOR Pathway: The Master Regulator of Muscle Growth
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a signaling pathway that acts as a molecular switch for muscle growth. When activated, mTOR directs cells to prioritize protein synthesis over breakdown, leading to muscle repair and hypertrophy.
How Is mTOR Activated?
- Amino Acids (Especially Leucine) – Leucine directly activates mTOR, signaling the body to start protein synthesis.
- Resistance Training – Exercise mechanically stresses muscle fibers, which also triggers mTOR activation.
- Growth Factors & Hormones – Insulin, IGF-1, and testosterone all support mTOR signaling.
When the mTOR pathway is activated, muscle cells increase protein production, leading to bigger, stronger muscles.
How Can You Maximize Muscle Protein Synthesis?
- Consume Enough Protein – Aim for 0.7–1.0 grams of protein per pound of body weight to optimize MPS.
- Time Your Protein Intake – Spreading protein across multiple meals (20–40g per meal) ensures constant MPS stimulation.
- Prioritize Leucine-Rich Foods – Animal proteins (chicken, beef, eggs, whey protein) and soy protein contain high amounts of leucine.
- Lift Heavy & Train Smart – Strength training is essential to trigger MPS.
- Avoid Long Periods Without Protein – A prolonged fasted state can lead to muscle breakdown, reducing net muscle gain.
When the mTOR pathway is activated, muscle cells increase protein production, leading to bigger, stronger muscles.
By understanding the mTOR pathway and MPS, you can make smarter training and nutrition choices to maximize muscle growth, recovery, and overall performance.
How Much Protein Do You Need?
Protein requirements vary depending on your activity level and goals. Here’s a breakdown:
Bodybuilders
For muscle growth, bodybuilders typically need 1.6–2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. This ensures they’re getting enough protein to stimulate MPS and promote recovery after intense training sessions.
Average Person
For the average person who isn’t actively trying to build muscle, the general recommendation is 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. This supports basic bodily functions and prevents muscle wasting.
Sedentary Individuals
Sedentary individuals may only need around 0.6–0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, as they are not engaging in significant physical activity or muscle repair needs.
What Happens If You Don’t Get Enough Protein?
Not getting enough protein can negatively impact muscle growth, recovery, and overall health.
- Muscle Loss & Weakness – Without enough protein, your body breaks down muscle for energy, leading to weakness and slower recovery.
- Slow Recovery & Injury Risk – Protein repairs muscle fibers; a deficiency increases soreness and injury risk.
- Weakened Immune System – Protein is essential for antibodies; low intake makes you more prone to illness.
- Hormonal Imbalances & Fatigue – Can cause low energy, mood swings, and metabolic issues.
- Hair, Skin, & Nail Problems – Leads to brittle hair, dry skin, and weak nails.
- Weakened Bones & Joints – Increases the risk of fractures and joint issues.
Protein Quality: Does It Matter?
Yes, protein quality matters. Complete proteins, which contain all 9 essential amino acids, are generally more effective for muscle growth. Animal-based proteins (like meat, eggs, and dairy) are complete proteins. Some plant-based proteins are incomplete, but when combined (e.g., beans and rice), they can form a complete amino acid profile.
The Best Protein Sources: Animal vs. Plant
Both animal-based and plant-based proteins can effectively support muscle growth, though there are some differences:
- Animal proteins (e.g., chicken, beef, eggs, fish) are complete and have a higher biological value, meaning your body can use them more efficiently.
- Plant-based proteins (e.g., lentils, quinoa, tofu, tempeh) may require careful planning to ensure you’re getting all the essential amino acids, but they’re still highly effective when consumed in variety
Is Protein Powder Bad for You?
Protein powder isn’t inherently bad, but some low-quality brands have issues:
- Artificial Sweeteners & Fillers – Some powders contain sucralose, aspartame, or sugar alcohols, which can cause bloating & gut issues.
- Heavy Metals & Contaminants – Some cheap powders may contain lead, arsenic, or mercury, especially in low-regulated brands.
- Low Digestibility – Whey concentrate or plant-based powders with fillers can cause bloating, gas, or stomach discomfort.
- Overprocessing – Some powders undergo excessive heating, reducing bioavailability (how well your body absorbs the protein).
🔹 How? Many powders cut costs by using poor-quality ingredients—always choose third-party tested, clean protein sources to avoid these issues.
7 Reasons People Supplement Protein
1. Muscle Growth & Recovery
– Helps repair and grow muscle after workouts.
2. Convenience
– Quick, easy way to meet protein needs without cooking.
3. Meeting Daily Protein Goals
– Essential for athletes, hardgainers, and vegetarians.
4. Fat Loss & Weight Management
– Increases fullness, reduces cravings, and preserves muscle.
5. Strength & Performance
– Enhances recovery, endurance, and power output.
6. Boosts Metabolism
– Burns more calories due to a higher thermic effect.
7. Supports Specialized Diets
– Ideal for vegans, elderly individuals, and those with dietary restrictions.
Best Protein Supplements:
- Whey – Fast-digesting, great for muscle recovery.
- Casein – Slow-digesting, best for nighttime.
- Plant-Based – Good for vegans and lactose-intolerant individuals.
- Egg Protein – High bioavailability and lactose-free.
When Should You Take Protein?
The timing of protein intake can optimize recovery. The most crucial time to take protein is post-workout, as the body is primed for muscle repair. Additionally, spreading protein intake evenly throughout the day can keep MPS elevated and support muscle recovery and growth.
How to Time Protein Intake with Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS)
Muscle protein synthesis (MPS) doesn’t stay elevated all day—it follows a spike-and-recover cycle, meaning proper timing of protein intake is crucial for maximizing muscle growth.
1. The Protein Feeding Window: How Often Should You Eat Protein?
- MPS spikes for 3–4 hours after a high-protein meal and then returns to baseline.
- Eating protein every 3–5 hours helps maintain an anabolic (muscle-building) state throughout the day.
🔹 Ideal Protein Distribution:
- 4–6 protein-rich meals per day
- 20–40g of protein per meal to maximize MPS activation
2. Key Protein Timing Strategies
🔹 Pre-Workout (30–90 Minutes Before Training)
✅ Why? Provides amino acids for muscle preservation & energy.
✅ What to eat? Lean protein (chicken, eggs, yogurt) + carbs for energy.
🔹 Post-Workout (Within 1–2 Hours After Training)
✅ Why? This is the prime anabolic window when MPS is most sensitive.
✅ What to eat? Fast-digesting protein (whey, eggs, lean meats) + carbs to replenish glycogen.
🔹Before Bed (Slow-Digesting Protein for Overnight Growth)
✅ Why? Prevents overnight muscle breakdown.
✅ What to eat? Casein protein (cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, casein shake) for sustained amino acid release.
🔹 First Meal of the Day (After Fasting Overnight)
✅ Why? Kickstarts MPS after an 8+ hour fast.
✅ What to eat? High-protein breakfast (eggs, protein shake, lean meats).
3. Does Fasted Training Hurt MPS?
Training on an empty stomach can reduce muscle retention, so consuming at least 10g of essential amino acids (EAA) or 20g of protein pre-workout is ideal.
Bottom Line: How to Optimize Protein Timing for MPS
✅ Eat 20–40g of protein every 3–5 hours
✅ Prioritize protein pre- & post-workout for best results
✅ Include slow-digesting protein before bed to sustain muscle growth overnight
By strategically timing protein intake, you can keep MPS elevated throughout the day, leading to better muscle gains and faster recovery.
How Protein Affects Recovery & Performance
Protein aids in muscle recovery by providing the amino acids necessary for muscle repair and growth, reducing muscle soreness, and enhancing glycogen replenishment. After a workout, protein helps to reduce the muscle damage caused by exercise, minimize inflammation, and accelerate recovery, allowing for better performance in subsequent workouts.
Protein for Fat Loss: Does It Still Matter?
Yes, protein is vital during a fat loss phase. When you’re in a calorie deficit, protein helps preserve lean muscle mass, prevent muscle breakdown, and increase satiety, which makes it easier to stick to your calorie goals. Higher protein intake may also elevate your metabolic rate, helping you burn more fat.
Does Protein Help You Lose Weight?
Yes, protein can aid in weight loss because:
- Boosts Metabolism – Digesting protein burns more calories (thermic effect of food (TEF)) than fats or carbs.
- Reduces Appetite – Protein increases satiety hormones (GLP-1, PYY, CCK) and decreases ghrelin (hunger hormone), making you feel fuller longer.
- Preserves Muscle – Prevents muscle loss during calorie deficits, keeping metabolism high.
🔹 How? A high-protein diet supports fat loss by keeping you full and maintaining muscle, both of which increase daily calorie burn.
The Role of Protein in Hormone Regulation
Protein plays a key role in hormone regulation, influencing hormones that control muscle growth, appetite, and metabolism. For example, protein affects the release of insulin (which helps with muscle protein synthesis) and ghrelin (a hormone that controls hunger).
Does Protein Help Endurance Athletes?
Yes, protein is important for endurance athletes as well. Although endurance activities primarily rely on carbohydrates, protein helps with muscle repair, prevents muscle breakdown, and supports recovery after prolonged physical activity. Endurance athletes should aim for 1.2–1.4 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight.
The Effects Of Too Much Protein
Can You Overconsume Protein?
While protein is essential, consuming excessive amounts (over 2.2 grams per kilogram) may put unnecessary strain on your kidneys over time, particularly if you have pre-existing kidney issues. However, for most healthy individuals, protein intake above 2.2 grams/kg is unlikely to have negative effects.
How Excess Protein Gets Stored as Fat
Your body prioritizes using protein for muscle repair, enzyme production, and energy when needed. But if you consume more protein than your body requires and you’re already getting enough energy from carbs and fats, the extra protein goes through these steps:
- Deamination – The body removes the nitrogen from excess amino acids, producing urea (which is excreted through urine).
- Energy Conversion – The remaining carbon skeletons of amino acids are either:
- Used for immediate energy (if needed).
- Converted into glucose through gluconeogenesis (if carbs are low).
- Converted into fat and stored in adipose tissue (if total calorie intake is too high).
Key takeaway: Protein itself isn’t stored as protein—if your body doesn’t need it, it turns into energy or fat.
Does Too Much Protein Cause Anxiety or Other Issues?
Excess protein doesn’t directly cause anxiety, but can contribute to it if:
- Amino Acid Imbalances – Overconsumption of certain amino acids (like tyrosine) may overstimulate dopamine and norepinephrine, leading to restlessness.
- Blood Sugar Fluctuations – Eating too much protein with too few carbs can trigger low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), which can cause mood swings and anxiety-like symptoms.
- Gut-Brain Connection – Digestive issues (bloating, discomfort) from low fiber + excessive protein may indirectly contribute to stress and mood imbalances.
🔹 How? Too much protein alone doesn’t cause anxiety, but imbalances in diet & digestion may play a role in stress levels.
Can Too Much Protein Cause Digestive Issues?
Yes, excess protein (especially from animal sources) can cause:
- Constipation – Low fiber intake from eating too much protein and not enough fiber-rich foods.
- Bloating & Gas – Undigested protein in the gut can ferment, causing bloating, gas, and discomfort.
- Kidney Strain (Only in Those with Preexisting Kidney Issues) – The body must filter excess nitrogen from protein breakdown, which may stress weak kidneys.
🔹 How? Protein digestion produces waste products (ammonia, urea)—if not processed efficiently, this can cause digestive discomfort.
Is Too Much Protein Bad for the Kidneys?
For healthy individuals, high protein intake does NOT cause kidney damage. However, for people with existing kidney disease, excess protein can:
✔ Increase kidney workload by producing more nitrogenous waste.
✔ Cause the kidneys to work harder to filter out excess urea.
✔ Worsen kidney function over time.
For most people, staying hydrated and balancing protein intake prevents any kidney stress
What About the Liver?
The liver processes amino acids, removing excess nitrogen and converting it into urea for excretion. If you overconsume protein, the liver has to work harder to:
✔ Break down excess amino acids.
✔ Convert protein into glucose for energy if needed.
✔ Remove nitrogen waste efficiently.
For healthy individuals, this isn’t a major issue. However, if you have liver disease, excess protein can:
❌ Increase ammonia buildup in the blood.
❌ Worsen liver function by overloading detox pathways.
Bottom Line: Too much protein isn’t dangerous for healthy kidneys or liver, but if you have pre-existing conditions, it’s best to moderate intake.
Protein FAQ:
1. Can I get enough protein without eating meat?
Yes, you can get sufficient protein from plant-based sources like legumes, nuts, seeds, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa. Combining different plant proteins ensures you get a complete amino acid profile.
2. Is protein required for fat loss?
Protein is crucial during fat loss as it helps preserve lean muscle mass, increase satiety, and boost metabolism. It can make the fat loss process more efficient while preventing muscle loss.
3. How much protein should I take to build muscle?
To build muscle, aim for 1.6–2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. This helps maximize muscle protein synthesis and ensures adequate recovery from workouts.
4. Can protein help me recover faster from intense workouts?
Yes, consuming protein post-workout provides the amino acids needed to repair muscle fibers and accelerate recovery. This reduces muscle soreness and prepares your muscles for the next workout.
5. Is there a best time to take protein?
The best time to take protein is within 30–60 minutes after a workout when your muscles are most receptive to repair and growth. Additionally, spreading protein intake throughout the day supports ongoing muscle recovery.
Key Takeaways:
- Protein is essential for muscle growth, repair, and recovery, and it supports overall health.
- Timing protein intake, particularly post-workout, optimizes muscle recovery.
- Protein helps preserve lean muscle mass and increase fat loss by boosting metabolism and promoting satiety.
- Both animal-based and plant-based proteins can meet your needs, though they may require careful planning in a plant-based diet.
- Consuming too much protein is generally not harmful unless it exceeds the body’s requirements for an extended period.
Sources:
Trending Articles:
Do you have any questions?




