The Science Behind Muscle Force Production
Introduction
How do muscles generate force? Whether you’re lifting heavy weights, sprinting, or even standing still, your muscles rely on complex physiological and biomechanical processes to produce movement. This guide breaks down the science of muscle force production in a clear, practical way—no unnecessary complexity, just the key concepts you need to know.
Understanding the mechanisms behind muscle force production is essential for optimizing performance, preventing injuries, and designing effective training programs. This article delves into the intricate processes that enable muscles to generate force, supported by research findings and biomechanical analyses.
Most average people only care about getting bigger muscles from pushing/pulling weight hoping to get bigger as a result when in reality their tempo sucks, their form is barely decent, and they don’t understand what they’re actually training for. I make this article for the people who want to know more than the average.
After reading this article you will have a strong understanding of what kind of muscle fibers do what, what type of hypertrophy you train for, proper tempo speed, motor units, what a sarcomere is and ideal sarcomere lengthening during a workout, ATP and how your body utilizes it, tendon stiffness, Rate of Force Development, and much more.
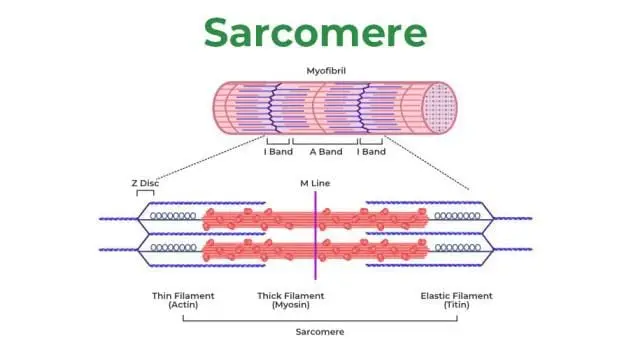
Table Of Contents
1. Motor Unit Recruitment and the Size Principle
2. Muscle Fiber Types and Their Contribution to Force Production
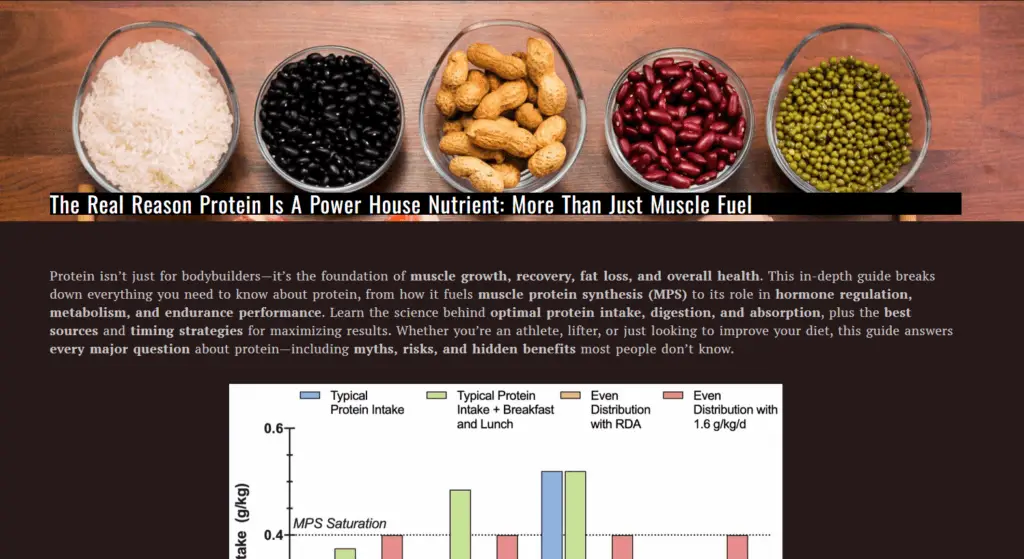
3. Sarcomere Length-Tension Relationship
4. Energy Systems Fueling Muscle Contraction
5. Force-Velocity Relationship in Muscle Contraction
6. Tendon Stiffness and Elastic Energy Storage
7. Neuromuscular Adaptations to Strength Training
8. Hypertrophy: Myofibrillar vs. Sarcoplasmic
9. Pennation Angle and Its Impact on Force Production
10. Rate of Force Development (RFD)
11. Stretch-Shortening Cycle (SSC) and Elastic Energy
12. Muscle Stiffness and Force Transfer
Conclusion
1. Motor Units and the Size Principle
Muscle force starts with motor units, which are made up of a motor neuron and the muscle fibers it controls. The size principle (Henneman’s principle) explains how they’re recruited:
Small motor units (slow-twitch fibers) activate first for low-intensity movements.
Larger motor units (fast-twitch fibers) kick in as intensity increases.
This ensures efficiency—why waste energy using large, powerful fibers when smaller ones can handle the job?
Motor Unit Recruitment Chart:
| Force Demand | Primary Fiber Type | Motor Unit Size |
|---|---|---|
| Low (e.g., standing, walking) | Type I (Slow-Twitch) | Small |
| Moderate (e.g., jogging, light lifting) | Type IIa (Fast-Twitch) | Medium |
| High (e.g., sprinting, heavy lifting) | Type IIx (Fast-Twitch) | Large |
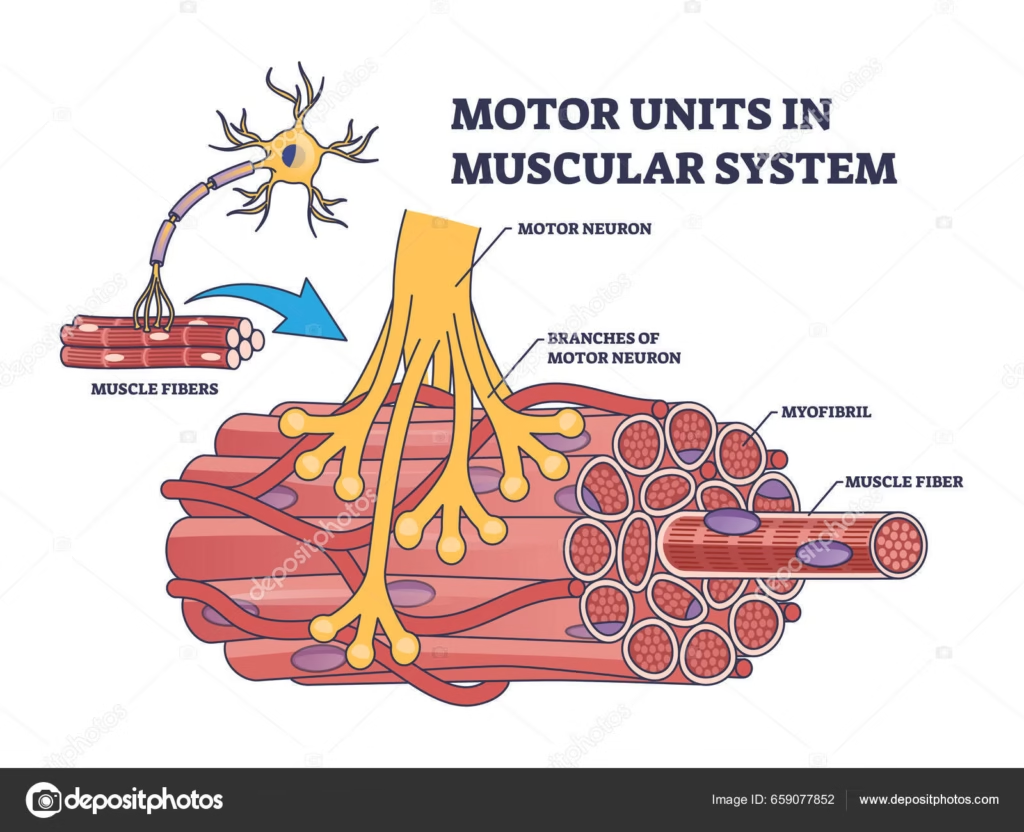
2. Muscle Fiber Types and Their Role in Force Production
Not all muscle fibers are built the same. There are three main types:
Type I (Slow-Twitch): Great for endurance, but not much force output.
Type IIa (Fast-Twitch, Oxidative-Glycolytic): A mix of endurance and power.
Type IIx (Fast-Twitch, Glycolytic): Built for short bursts of maximum force but fatigue quickly.
Comparison of Muscle Fiber Types:
| Fiber Type | Contraction Speed | Force Output | Fatigue Resistance | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type I | Slow | Low | High | Marathon Running |
| Type IIa | Fast | Moderate | Moderate | Sprinting, Cycling |
| Type IIx | Very Fast | High | Low | Heavy Lifting, Jumping |
3. The Length-Tension Relationship
Muscle force depends on how stretched or contracted the sarcomere (the muscle’s smallest functional unit) is. There’s an optimal length where force production is at its highest.
Too short: The muscle is cramped, reducing force.
Too stretched: The filaments can’t connect properly, reducing force.
Optimal range (2.0–2.2 µm sarcomere length): Maximum force output.
Practical Example:
A deep squat might reduce force if the quads are overstretched.
A half-squat might be better for max force output due to a more optimal muscle length.
4. Energy Systems and Muscle Force
Your muscles don’t work without energy. Different energy systems fuel force production depending on intensity and duration:
| Energy System | Primary Fuel | Duration | Example Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATP-PCr (Phosphagen) | Stored ATP | 0-10 sec | Sprinting, Heavy Lifting |
| Glycolysis (Anaerobic) | Carbohydrates | 10 sec – 2 min | 400m Sprint, HIIT |
| Oxidative (Aerobic) | Fat/Carbs | 2 min+ | Long-Distance Running |
Related Articles
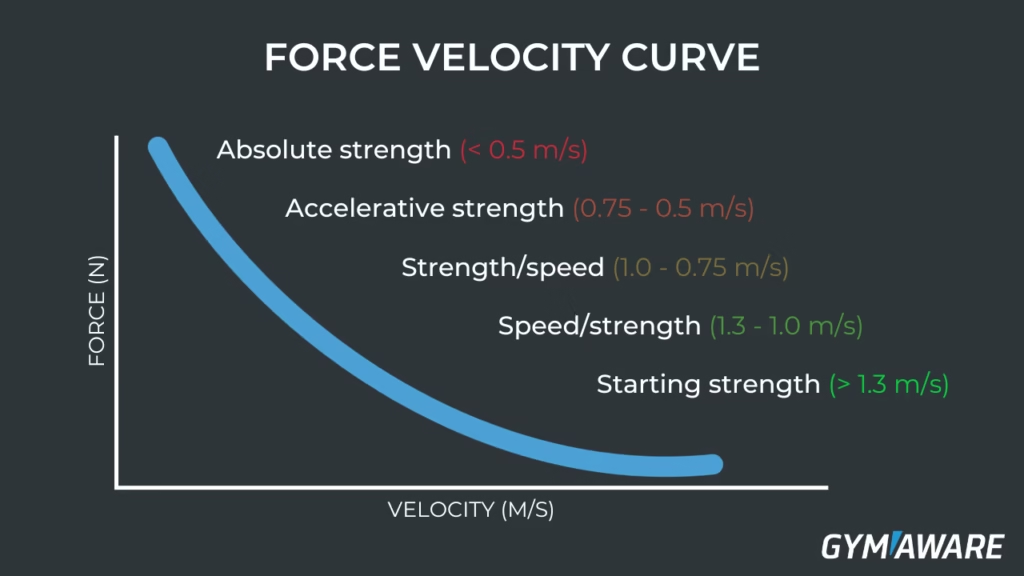
5. The Force-Velocity Relationship
The faster a muscle contracts, the less force it can generate. This is why you can lift more weight slowly but struggle to move heavy loads quickly.
Slow, heavy movements (e.g., deadlifts) = high force, low speed.
Fast, explosive movements (e.g., jumping) = low force, high speed.
Force-Velocity Curve:
6. Rate Coding and Muscle Firing Frequency
Muscles increase force not just by recruiting more motor units but by increasing how fast they fire. This is known as rate coding.
Low-frequency firing: Produces smooth, sustained contractions.
High-frequency firing: Allows for explosive, powerful contractions.
Example:
A powerlifter needs high rate coding to generate max force in a short time.
A marathon runner benefits from lower firing rates to maintain endurance.
7. Stretch-Shortening Cycle (SSC) and Elastic Energy
The Stretch-Shortening Cycle (SSC) is a powerful mechanism by which muscles store elastic energy during an eccentric (lengthening) phase and then release it during a concentric (shortening) phase, producing greater force. This principle is commonly used in dynamic, high-force movements.
Eccentric phase: Muscle lengthens, storing energy (e.g., squatting before a jump).
Concentric phase: Energy is released to produce force (e.g., jumping upward).
Practical Example:
A countermovement jump (bending knees before jumping) produces more force than a static jump because of stored elastic energy.
8. Muscle Stiffness and Force Transfer
Muscle stiffness refers to the resistance muscles provide against deformation under force. Stiffness is crucial for optimal force transfer—when muscles are more stiff, they can generate and transfer force more efficiently to the bones, enhancing performance in explosive movements.
Greater stiffness: Improved force transfer, better power output.
Lower stiffness: More compliance, reducing force transfer efficiency.
Example:
– A sprinter’s hamstrings need high stiffness to transfer force efficiently during each stride.
– Jumping athletes rely on high stiffness in their calves to maximize force transfer during take-off.
9. Neuromuscular Adaptations to Strength Training
Lifting weights does more than grow muscles—it rewires your nervous system to produce more force. Over time, your body adapts by:
Increasing motor unit recruitment (activating more muscle fibers at once).
Boosting firing frequency (neurons send stronger, faster signals).
Reducing neural inhibition (overcoming built-in limits that prevent maximum effort).
These changes make you stronger before you even build muscle mass—this is why beginners see rapid strength gains in their first few weeks of training.
10. Pennation Angle and Its Effect on Force Production
Muscle fibers don’t always run in straight lines—they often angle toward the tendon (pennation). A higher angle means more fibers can fit, increasing force production but slightly reducing speed.
Example:
The quadriceps have a high pennation angle, making them powerful but not super fast.
The hamstrings have long, parallel fibers, making them faster but slightly weaker.
11. Rate of Force Development (RFD)
How quickly can your muscles produce force? This is crucial for sports requiring explosive power.
Powerlifting focuses on max force but slower contractions.
Olympic lifting and sprinting focus on producing force as fast as possible.
Training explosive movements like jumps, sprints, and Olympic lifts can dramatically improve RFD.
Conclusion
Muscle force production is a complex, dynamic process influenced by motor units, muscle fiber types, biomechanics, and neuromuscular adaptations. Understanding these principles can help you train smarter—whether your goal is strength, speed, or endurance.
Key Takeaways:
Motor unit recruitment follows the size principle—small first, large as intensity increases.
Muscle fibers are specialized for endurance, power, or explosive force.
The length-tension relationship and force-velocity curve influence strength and speed.
Tendon stiffness, energy systems, and neuromuscular efficiency all impact performance.
By applying these principles, you can optimize your training for maximum performance and efficiency.
FAQ: Muscle Force Production
1. What is muscle force production?
Muscle force production is the ability of a muscle or muscle group to generate tension and create movement. It involves the recruitment of motor units, activation of muscle fibers, and coordination of the nervous system. The more efficiently these systems work together, the more force your muscles can produce.
2. What are motor units and why are they important?
A motor unit consists of a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it controls. They’re crucial for force production because more motor units (and larger ones) are recruited as the demand for force increases. This follows the size principle—small, slow-twitch motor units activate first, followed by larger, fast-twitch units.
3. How do slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscles affect force?
Slow-twitch muscles (Type I) are built for endurance and continuous effort but produce low force.
Fast-twitch muscles (Type II) contract quickly and powerfully, making them ideal for explosive force production.
Training can influence the balance and efficiency of these twitch muscles for your specific goals.
4. What are neuromuscular adaptations and how do they affect strength?
Neuromuscular adaptations refer to changes in how your nervous system and muscles communicate. As you train, your body learns to:
Recruit more motor units
Fire them faster and more efficiently
Overcome natural inhibitors that limit force These adaptations boost strength and power, even before muscle size increases.
5. How does muscle fiber type influence training results?
Different muscle fiber types respond differently to training:
Type I fibers respond best to high-rep endurance training.
Type II fibers thrive under heavy loads, explosive reps, and shorter durations. Understanding your dominant fiber types can help tailor your training for optimal force production.
6. What is the stretch-shortening cycle and how does it help with performance?
The Stretch-Shortening Cycle (SSC) is when a muscle rapidly lengthens (eccentric phase) and then immediately shortens (concentric phase), storing and releasing elastic energy. It enhances force output in movements like jumping, sprinting, or rebounding from a lift.
7. How does stiffness affect force production?
Muscle and tendon stiffness improve the efficiency of force transfer. A stiffer muscle-tendon unit stores and releases force more effectively, leading to better performance in high-power movements like sprinting and jumping.
8. Can you increase muscle force without gaining muscle size?
Yes. In the early stages of training, most strength gains come from neuromuscular adaptations rather than muscle growth. Improving coordination, motor unit recruitment, and firing rate can increase force production without a visible size increase.
9. What’s the difference between force and power in muscles?
Force is the amount of tension a muscle can produce.
Power is how quickly that force can be applied (Force × Velocity). You can be strong but slow (high force, low power), or explosive but not necessarily strong (high power, moderate force).
10. How can I train to maximize muscle force production?
Focus on:
Heavy resistance training for max strength
Plyometrics for stretch-shortening cycle efficiency
Speed training for rate of force development
Isometrics and eccentrics to build tendon stiffness
Gradually increasing intensity to recruit more motor units
Trending Articles:
Do you have any questions?