Why Do People Supplement Protein?
Protein is the foundation of muscle growth, recovery, and overall health, but getting enough from food alone can be challenging. That’s why many people turn to protein supplements—they’re a convenient, efficient way to meet daily protein needs and maximize muscle-building results. But why exactly do people supplement with protein, and what should you look out for when choosing the best option? Let’s break it down.
What Is Protein?
Protein is a macronutrient essential for muscle growth, repair, and overall body function. It’s made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of muscle tissue. Some amino acids are essential, meaning your body can’t produce them and must get them from food or supplements.


Protein plays a crucial role in:


Since muscles break down and rebuild constantly, getting enough high-quality protein is key to maximizing results—whether through whole foods or supplementation.


The Science Behind Protein & Muscle Growth
When you work out, you create tiny tears in your muscle fibers. Your body repairs and rebuilds these fibers stronger and thicker through a process called muscle protein synthesis (MPS). To fuel this process, your body needs a steady supply of high-quality protein. Jump to protein timing
Why Protein Supplements Help
✅ Provides essential amino acids – Supports faster muscle repair & growth
✅ Boosts muscle protein synthesis – Helps rebuild muscle stronger after workouts
✅ Prevents muscle breakdown – Ensures your body has enough protein to maintain muscle mass
✅ Convenient & efficient – Ideal for people with busy schedules who struggle to hit their protein goals through food alone

The Best Whey Protein
25g Protein, Great Taste, Low Sugar. 7 different flavors, 4 different sizes

The Best Plant Protein
21g Plant Protein, 6g Prebiotic Fiber, No Lactose Ingredients, No Added Sugar,
Top Reasons People Supplement Protein
1. To Build & Repair Muscle Faster
After intense exercise, your muscles need a fast-digesting protein source to repair and grow. Whey protein is popular because it’s quickly absorbed and rich in leucine, an amino acid that directly triggers muscle protein synthesis.
2. To Meet Daily Protein Requirements
Not everyone can eat enough high-protein foods every day. Protein supplements help fill the gaps, especially for:
✔ Athletes & bodybuilders who need extra protein to recover
✔ Vegans & vegetarians who may lack complete protein sources in their diet
✔ Busy individuals who don’t have time to prepare multiple high-protein meals
3. To Support Fat Loss While Maintaining Muscle
Protein helps preserve muscle mass while burning fat by:
🔥 Increasing satiety – Makes you feel full longer, reducing cravings
🔥 Boosting metabolism – Requires more energy to digest compared to fats & carbs
🔥 Preserving lean muscle – Prevents muscle loss during calorie deficits
4. To Improve Recovery & Reduce Soreness
Protein supplementation helps:
💪 Reduce muscle soreness after workouts
💪 Speed up recovery so you can train harder, more often
💪 Prevent excessive muscle breakdown, keeping you stronger over time
5. For Convenience & Versatility
Drinking a protein shake is much faster than cooking a meal. Plus, protein powders can be added to smoothies, oatmeal, or baked goods for extra nutrition.
6. To Support Specific Health Goals
Protein supplements can also help with:
✔ Aging & muscle preservation – Prevents muscle loss as you get older
✔ Healing injuries – Helps repair tissues faster
✔ Supporting overall health – Boosts immune function & hormone production
What to Look Out for When Buying Protein Supplements
Not all protein supplements are created equal. Some contain unwanted additives, low-quality ingredients, or misleading claims that can negatively impact your health and gains. Here’s what to watch out for when choosing a high-quality protein supplement:
🚨 1. Artificial Sweeteners & Fillers
Some protein powders are loaded with artificial sweeteners like:
❌ Sucralose – Can cause digestive issues in some people
❌ Aspartame – Controversial due to potential health risks
❌ Acesulfame K – Often used to enhance sweetness but may have negative effects
🔎 What to choose instead:
✅ Stevia or monk fruit as natural sweeteners
✅ Unsweetened protein powders with minimal ingredients
🚨 2. Low-Quality Protein Blends & Amino Spiking
Some companies cut costs by adding low-quality proteins or using amino spiking (adding cheap amino acids instead of complete protein).
⚠️ Red flags:
❌ Protein blends with “proprietary formulas” (hides exact amounts of each protein)
❌ Amino spiking (high amounts of glycine, taurine, or creatine listed instead of complete protein)
🔎 What to choose instead:
✅ 100% whey isolate, casein, or plant-based proteins with no fillers
✅ Look for products with transparent labeling and third-party testing
🚨 3. Heavy Metals & Contaminants
Some protein powders, especially lower-quality brands, have been found to contain unsafe levels of heavy metals like:
❌ Lead – Toxic in high amounts
❌ Arsenic – Linked to long-term health issues
❌ Cadmium & Mercury – Can accumulate in the body over time
🔎 What to choose instead:
✅ Certified third-party tested brands (look for NSF, Informed Choice, or USP certification)
✅ Organic or high-quality protein sources
🚨 4. Unnecessary Additives & Thickeners
Some protein powders include artificial thickeners and emulsifiers to improve texture, but they may cause digestive discomfort.
❌ Carrageenan – Linked to inflammation and gut issues
❌ Xanthan gum & guar gum – Can cause bloating in sensitive individuals
🔎 What to choose instead:
✅ Minimal-ingredient protein powders
✅ Natural thickeners like sunflower lecithin instead of synthetic ones
🚨 5. Poor-Quality Protein Sources
Not all protein sources are high-quality. Some protein powders use inferior sources or have low bioavailability, meaning your body doesn’t absorb them well.
⚠️ Watch out for:
❌ Collagen protein as a primary ingredient (great for skin/joints, but not for muscle growth)
❌ Rice protein as the sole protein (incomplete amino acid profile)
❌ Cheap whey concentrate with excessive fat & lactose
🔎 What to choose instead:
✅ Whey isolate or hydrolyzed whey for highest absorption
✅ Pea + rice protein blends for plant-based complete protein
✅ Egg protein for a high-quality alternative to dairy
🚨 6. High Sugar & Unnecessary Carbs
Some protein powders contain excessive sugar or hidden carbs to improve taste, which can be bad for lean muscle gain or fat loss goals.
⚠️ Avoid:
❌ Protein powders with more than 5g of sugar per serving
❌ “Mass gainers” filled with cheap carbs and maltodextrin
🔎 What to choose instead:
✅ Low-sugar or unsweetened protein powders
✅ If carbs are needed, pair with whole foods like oats or fruit
While whole foods should always be your primary protein source, supplements are an easy, effective way to support muscle growth, recovery, and overall health.
🔥 Looking for the best protein supplements? Check out our top picks:
✅ Best Whey Protein for Muscle Growth – [Affiliate Link]
✅ Best Plant-Based Protein – [Affiliate Link]
✅ Best Clean Protein with No Fillers – [Affiliate Link]

Sources of Animal Protein
- Chicken Breast – Lean and versatile, chicken breast is a top choice for muscle building and recovery.
- Turkey – Another lean poultry option, rich in protein and low in fat.
- Eggs – A complete protein source with all essential amino acids; ideal for muscle repair and growth.
- Lean Beef – Provides high-quality protein along with important nutrients like iron and B vitamins.
- Fish – Varieties like salmon, tuna, and cod are excellent sources of protein and offer heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
- Greek Yogurt – Higher in protein compared to regular yogurt, great for snacks or breakfast.
- Cottage Cheese – High in casein protein, which is slowly digested and supports muscle recovery over time.
- Milk – A complete protein source that also provides calcium and vitamin D
Sources of Plants Protein
- Lentils – Rich in protein and fiber, making them a great choice for vegetarians and vegans.
- Chickpeas – Versatile and protein-packed; great in salads, stews, or as a base for hummus.
- Quinoa – A complete plant protein containing all essential amino acids, perfect as a base for various dishes.
- Tofu – Made from soybeans, tofu is a complete protein and can be used in a variety of recipes.
- Tempeh – Fermented soy product with a nutty flavor and high protein content, excellent for stir-fries and salads.
- Edamame – Young soybeans that are high in protein and make for a nutritious snack or addition to meals.
- Hemp Seeds – Rich in protein and healthy fats; can be added to smoothies, salads, or yogurt.
- Chia Seeds – Packed with protein and omega-3 fatty acids, great for adding to puddings or smoothies.
Protein Supplements
- Whey Protein – Quickly absorbed and ideal for post-workout recovery; rich in BCAAs for muscle growth.
- Casein Protein – Slowly digested, providing a sustained release of amino acids; great for nighttime recovery.
- Egg White Protein – High in bioavailability, dairy-free, and a complete protein source.
- Collagen Protein – Supports joint, skin, and connective tissue health but lacks essential amino acids for muscle building.
- Milk Protein Isolate – A blend of whey and casein, offering both fast and slow digestion for all-day muscle support.
- Pea Protein – A high-quality plant-based protein that is easily digestible and great for those with dairy sensitivities.
- Rice Protein – Often combined with pea protein to create a complete amino acid profile; hypoallergenic and easy to digest.
- Hemp Protein – Contains essential fatty acids and fiber but lower in protein compared to other plant sources.
- Soy Protein – A complete plant-based protein with all essential amino acids, though some avoid it due to concerns over phytoestrogens.
- Pumpkin Seed Protein – Rich in minerals like magnesium and zinc; a great allergen-friendly alternative.
- Algae Protein – A sustainable source of plant protein, rich in omega-3 fatty acids and micronutrients.
- Beef Protein Isolate – A dairy-free alternative made from hydrolyzed beef, often used in paleo diets.
How Much Protein Do You Need for Muscle Growth?
Getting the right amount of protein is crucial for building muscle, repairing tissue, and maximizing performance. But how much do you really need? The answer depends on factors like your goals, body weight, and activity level.
How Much Protein Do You Need Per Day?
General Protein Recommendations





How Protein Needs Change Based on Goals
✅ For Muscle Growth & Strength Gains
- Aim for 0.7–1.0g per pound of body weight.
- Spread protein intake evenly across meals to maximize muscle protein synthesis.
- Best timing: Post-workout protein helps recovery and muscle repair.
🔥 For Fat Loss While Maintaining Muscle
- Increase protein intake to 1.0–1.2g per pound to preserve muscle while cutting fat.
- Protein keeps you full longer and helps prevent muscle loss during a calorie deficit.
⚡ For Endurance & Athletes
- Runners, cyclists, and endurance athletes need 0.6–0.9g per pound to support muscle recovery and performance.
- Protein helps prevent excessive muscle breakdown from long training sessions.
General Macro Guide
Bodybuilders: High protein, low carbs, and high fat diet
Powerlifters: High protein and high carbs
Athletes: High protein, balanced carbs, high fat
Protein and Hypertrophy
Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS): Hypertrophy occurs when the rate of muscle protein synthesis (MPS) exceeds the rate of muscle protein breakdown (MPB). Protein provides the essential building blocks, known as amino acids, that are required for MPS. During resistance training, muscle fibers undergo stress and damage, triggering the body to repair and reinforce these fibers, making them larger and stronger. Adequate protein intake ensures that the body has a sufficient supply of amino acids to support this process.
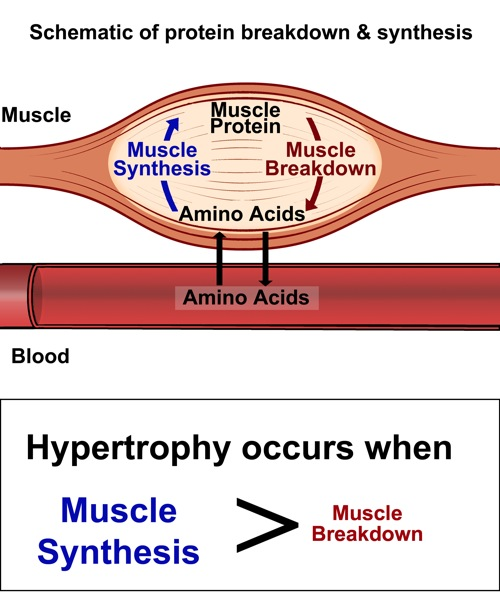
Protein's Role In Hypertrophy
To optimize hypertrophy, it’s important to meet daily protein requirements consistently. While exact needs can vary based on factors like body weight, activity level, and individual goals, a common guideline for those looking to build muscle is to consume about 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. Distributing protein intake evenly across meals can help maintain a steady supply of amino acids, supporting continuous muscle growth
Leucine’s Role: Among the essential amino acids, leucine plays a particularly critical role in hypertrophy. Leucine acts as a key signal for initiating MPS, essentially turning on the muscle-building process. Ensuring that your diet includes sufficient leucine, whether through whole foods or supplements, can significantly enhance muscle growth.
When Should You Eat Protein?
The timing of protein intake is also important for maximizing hypertrophy. Consuming protein before and after workouts provides a steady stream of amino acids that can be used for muscle repair and growth. This strategy helps to ensure that MPS remains elevated during the crucial recovery period following exercise.
Make sure you eat a good hardy meal before you do anything physically and time consuming. Eating high quality meals will increase your work output, your stamina and strength will increase, and your motivation wont be anything to worry about.

Can You Eat Too Much Protein?
Many believe “more protein = more muscle”, but your body can only use so much at a time.
❌ Excess protein won’t turn into more muscle—it’s either used for energy or stored as fat.
❌ Too much protein without enough water can stress your kidneys.
✅ Stay hydrated and balance protein with carbs & fats for optimal results.
Ideal Protein Intake Per Meal:
- 20–40g of protein per meal is optimal for stimulating muscle growth.
- Anything beyond 40g in one sitting won’t provide extra benefits.
Final Thoughts: How Much Protein Do You Really Need?
If you’re serious about muscle growth:
✔ Eat 0.7–1.0g per pound of body weight.
✔ Distribute protein across the day (not just post-workout).
✔ Prioritize high-quality sources (lean meats, eggs, dairy, plant-based protein).
✔ Stay consistent – muscle growth takes time and proper nutrition.
🔹 Want to know the best protein sources to hit your daily intake? Check out: [Best Protein Sources for Muscle Growth]
🔥 Best Animal-Based Protein Powders
Whey Protein Powder
What is Whey?
Whey protein is a high-quality protein derived from milk during the cheese-making process. When milk is curdled, it separates into curds (used for cheese) and whey, a liquid byproduct that contains proteins, lactose, vitamins, and minerals. This whey is then processed and refined to create whey protein powder, which is widely used as a dietary supplement.
✔ Type: Whey Isolate & Concentrate Blend
✔ Why It’s the Best:
- High-quality protein (25g per serving)
- Low fat & carbs (ideal for lean muscle growth)
- Rich in BCAAs for muscle recovery
✔ Best For: Fast post-workout recovery & muscle gain - Less Than 1g of sugar per serving

The Best Whey Protein
25g Protein, Great Taste, Low Sugar. 7 different flavors, 4 different sizes
Casein Protein Powder
What is Casein?
Casein protein, like whey, is derived from milk and is known for its slow digestion and absorption rate. This makes it an excellent option for providing a steady release of amino acids, making it a popular choice for muscle maintenance and recovery, especially during periods of fasting, such as overnight.
✔ Type: Micellar Casein
✔ Why It’s the Best:
- 24g of slow-digesting protein per serving
- Great for overnight muscle repair
✔ Best For: Nighttime recovery & long-lasting protein intake
Egg White Protein Powder
What is Egg Protein?
Egg protein is extracted from the whites of eggs, which are naturally low in fat and carbohydrates but high in protein. Unlike the yolk, egg whites contain minimal cholesterol, making egg protein an ideal choice for those who are health-conscious or following a low-fat diet. It is also lactose-free, providing a suitable alternative for those with dairy sensitivities.
✔ Type: 100% Egg White Protein
✔ Why It’s the Best:
- Dairy-free & easy to digest
- High bioavailability (22g protein per serving)
✔ Best For: Lactose-intolerant athletes needing a complete protein
Collagen Protein Powder
What is Collagen Protein?
Collagen protein is sourced from animal connective tissues and is primarily used for supporting joint, skin, and hair health rather than muscle building. It lacks some essential amino acids found in complete proteins, but it is rich in glycine and proline, which contribute to overall tissue repair. Collagen is easily digestible and dairy-free, making it a good option for those with dietary restrictions.
✔ Type: Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides
✔ Why It’s the Best:
- Great for joint health, skin, and recovery
- Dissolves easily in any drink
✔ Best For: Joint support & anti-aging benefits
🌱 Best Plant-Based Protein Powders
What Are They?
Plant-Based Proteins are proteins derived from plants, including sources like legumes, grains, seeds, nuts, and vegetables. Unlike animal-based proteins, which come from meat, dairy, and eggs, plant-based proteins are obtained from various plant foods that are naturally rich in protein.
Vegan Protein Powder
✔ Type: Pea, Rice, & Chia Seed Protein
✔ Why It’s the Best:
- Complete protein with all essential amino acids
- Organic & clean ingredients
✔ Best For: Plant-based muscle building
The Best Vegan Protein
21g Plant Protein, 7g Prebiotic Fiber, Low Net Carb, No Lactose, No Added Sugar
Pea Protein Powder
What is Pea Protein?
Pea protein is made from yellow peas and is a high-quality plant-based protein that is naturally rich in essential amino acids, particularly arginine. It is highly digestible, free from common allergens like dairy and soy, and often used in vegan protein blends. While slightly lower in methionine, it is commonly paired with other plant proteins to create a complete amino acid profile.
✔ Type: 100% Yellow Pea Protein
✔ Why It’s the Best:
- High in BCAAs (27g protein per serving!)
- No artificial sweeteners or additives
✔ Best For: Vegan muscle growth
The Best Pea Protein
Unflavored Vegan Pea Protein Isolate – Plant Protein Powder 5LB 100% Pea Protein Powder
Rice Protein Powder
What is Rice Protein?
Rice protein is extracted from brown rice and serves as a great plant-based protein alternative. It is naturally hypoallergenic and easy to digest, making it suitable for those with food sensitivities. While it is lower in lysine, it is often combined with pea protein to create a more balanced and complete amino acid profile.


- Easy to digest & gentle on the stomach
- Mixed with pea-based proteins for a complete amino acid profile
Best For: Weight loss & digestion support
Vegan & Keto Friendly | Gourmet Flavors with No Bloating or Stomach Upset
Hemp Protein Powder
What is Hemp Protein?
Hemp protein is derived from hemp seeds and is a plant-based protein that naturally contains omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and essential minerals. While it is not a complete protein due to lower lysine levels, it provides additional health benefits, such as heart and digestive support. Its earthy flavor and nutrient-dense profile make it a popular choice among health-conscious individuals.
✔ Type: 100% Hemp Protein
✔ Why It’s the Best:
- Rich in fiber, omega-3s, and minerals
- Best plant-based protein for overall nutrition
✔ Best For: Overall health & heart benefits
Hemp Protein Powder
What is Hemp Protein?
Soy protein is extracted from soybeans and is one of the few complete plant-based proteins, containing all nine essential amino acids. It has been widely studied for its muscle-building properties and is a common alternative to dairy-based proteins. Some people may prefer to avoid soy due to its phytoestrogen content, but it remains a high-quality, versatile protein source.


- AMAZING TASTE
- Only 130 calories and 13g of plant protein provide long-lasting satiation
- LACTOSE & GLUTEN FREE
13g Protein & 130 Calories per Servings – Zero Trans Fat – Non-GMO Soy – Lactose & Gluten Free
How to choose which one is right for you
Determine your goals
Before choosing a protein powder, it’s important to determine your personal fitness and health goals. Whether you’re aiming to gain muscle, improve general health, or lose weight, your goal will guide you to the best type of protein. For example, if your main goal is muscle gain, you may need a protein that provides a high amount of fast-absorbing protein, such as whey or casein. On the other hand, if you’re focused on weight loss, a low-calorie option like egg white or plant-based protein can help you maintain muscle while cutting calories. Understanding your specific needs will ensure that you’re choosing the right protein supplement that aligns with your lifestyle, diet, and overall fitness journey.
Muscle Building
Using Bulking Powder with whey protein isolate tends to be the best route when trying to build muscle. Bulking powder is packed full of dense nutrients that are high in calories, fueling you for your day full of intense training! If your goal is to build as much muscle as possible I would recommend sticking to whey isolate or upgrading to bulk powder. YOU WILL MOST LIKELY GAIN WEIGHT WHEN TAKING BULK POWDER!
Whey Protein Isolate provides:
- High Protein Content: Typically around 90% protein by weight.
- Rapid Absorption: Ideal for post-workout recovery to quickly supply muscles with essential amino acids.
- Rich in BCAAs: Supports muscle growth and repair effectively
Weight loss
When trying to lose weight definitely aim for fewer calories overall, something that fills you up for long, a speedy absorption of nutrients, and a dense amount of nutrients. When it comes to all of that Whey protein isolate takes to top spot. It’s so little calories for what it is, and supports lean muscle growth and weight loss. If you are wanting a plant protein to choose from I would recommend pea protein. Last but not least egg white protein is low in calories and fat while being rich in high-quality, complete protein, which makes it effective for preserving lean muscle mass during weight loss. Its slower digestion compared to whey can help keep you feeling fuller for a longer period, reducing overall calorie intake.
General Health
Casein Protein provides:
- Slow Digestion: Helps keep you full for longer periods, reducing overall calorie intake.
- Supports Muscle Preservation: Helps retain muscle mass during weight loss.
Low in Carbs and Fat: Most casein protein powders are low in carbohydrates and fats, making them suitable for a weight loss diet. They provide high-quality protein without excess calories from carbs and fats
Whey Protein Isolate is nutrient dense and contains additional nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and vitamins, which contribute to bone health and overall wellness.
Plant Based Proteins often contain fiber, which supports a healthy digestive system.
Check The Ingredients
Reading the ingredients on protein powders is essential to ensure you’re getting a product that aligns with your dietary needs and health goals. Ingredients lists reveal the quality of the protein source, the presence of any additives, sweeteners, or allergens, and whether the product is free from unnecessary fillers. By checking the ingredients, you can make sure you’re choosing a clean, effective supplement that supports your fitness journey without any unwanted surprises
Read Reviews
Reading reviews on protein powders is crucial for making an informed decision about which product best suits your health and fitness goals. Reviews provide real-world insights from users who have already tried the product, giving you a better understanding of its effectiveness, taste, and potential side effects. Unlike marketing materials, which often highlight only the positives, reviews can offer a balanced perspective, revealing both the strengths and weaknesses of a protein powder. This can help you avoid wasting money on products that don’t deliver on their promises.
Can you have too much protein?
You can have too much protein, and while it’s essential for muscle growth, repair, and overall health, consuming excessive amounts can lead to issues. High protein intake over extended periods may put strain on the kidneys, cause dehydration, and result in nutrient imbalances if other food groups are neglected.
It’s important to find the right balance based on your body’s needs, fitness goals, and activity levels to avoid negative health effects while still benefiting from protein’s many advantages.
Common Protein Deficiencies
Protein deficiencies are common due to the foods people eat, and the processed foods sold in stores. People who don’t get enough protein may experience thinning hair, brittle nails, or even fluid retention, which causes swelling in certain areas of the body. Protein deficiencies can have serious effects on your body, leading to muscle loss, weakened immunity, fatigue, and slowed recovery from injuries.
To avoid protein deficiency, it’s essential to include a variety of protein sources in your diet, such as lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, and plant-based proteins like beans and nuts. Monitoring your daily intake and supplementing when necessary can help ensure you’re meeting your body’s needs, especially if you’re highly active or have specific health conditions. A balanced diet rich in protein not only helps maintain muscle mass but also keeps your energy levels stable and supports long-term health.
Muscle Loss or Weakness: Without enough protein, your body starts to break down muscle tissue, leading to muscle wasting and weakness.
Fatigue: Protein is crucial for energy production; low levels can cause constant tiredness and lack of stamina.
Hair, Skin, and Nail Problems: Hair thinning, brittle nails, and dry, flaky skin are common when your body lacks the necessary building blocks for healthy cells.
Frequent Infections or Illness: Protein plays a key role in supporting your immune system, so deficiency can make you more prone to infections.
Slow Healing of Wounds: A lack of protein can impair your body’s ability to repair tissues, leading to slower recovery from injuries.
Fluid Retention (Edema): Protein helps maintain proper fluid balance; a deficiency can lead to swelling, especially in the feet, ankles, and legs.
Cravings and Hunger: Low protein levels can increase hunger, especially for sweets and carbs, as the body seeks to compensate for missing nutrients.
How to use protein supplements
Protein supplements usually come in powdered form. The powder can be mixed with many things like to incorporate more protein into your diet. Usually people mix the powder with water or mix and mix it up or blend it with stuff like fruit to make a protein smoothie.
Post-Workout Recovery: After intense exercise, your muscles need protein to repair and grow. Protein powders, especially fast-digesting options like whey, can be an excellent way to quickly deliver essential amino acids to your muscles.
Meal Replacement: If you’re on the go or don’t have time for a full meal, protein powders can serve as a convenient substitute. Mix with water or milk, and add ingredients like fruits or oats to make a balanced shake that keeps you full and nourished.
Boost Daily Protein Intake: If you struggle to meet your daily protein needs through whole foods, adding a protein shake to your regular meals can ensure you’re getting enough. This is particularly helpful for athletes, bodybuilders, or anyone with higher protein requirements.
Pre-Workout Fuel: Some people prefer a protein shake before exercise to provide their body with the nutrients it needs during a workout. A protein supplement can give you steady energy, especially when combined with carbs.
Nighttime Recovery: Slow-digesting protein powders, such as casein, are ideal before bed to provide your muscles with a continuous source of protein throughout the night, supporting recovery as you sleep.
So, Why Do People Supplement Protein?
People supplement protein to support muscle growth, recovery, and overall health. Whether it’s for building muscle, improving workout performance, managing weight, or filling dietary gaps, protein supplements offer a convenient and effective way to meet daily protein needs. With various types available, from whey to plant-based options, choosing the right supplement depends on individual goals and dietary preferences.
Trending Articles:
Do you have any questions?


 Best Whey Protein – Animal Isolate Loaded Whey Protein
Best Whey Protein – Animal Isolate Loaded Whey Protein








