The Optimized Muscle Group Split: A Revolutionary approach designed to maximize your gains
Workout Generator
Your Ultimate Workout Routine

Table Of Contents
- Workout Generator
How to Understand Your Routine
2.1 Extended Rest for Maximum Recovery
2.2 What’s more important, Systematic recovery or muscle recovery?
2.3 Muscle Recovery: Repairing Local Damage
2.4 Systemic Recovery: The Bigger Picture
2.5 Which One Should You Prioritize?
3. How Extended Rest Translates to Gains:
3.1 Increased Volume for Superior Muscle Stimulation
3.2 Why Increased Volume Matters:
4. Improved Intensity with Full Focus
4.1 Balanced and Strategic Progression
4.2 Implementing Strategic Progression
5. How BodyBuilding, Powerlifting, and Calisthenics routines differ
5.1 Bodybuilding: Focus on Aesthetics and Muscle Growth
5.2 Powerlifting: Focus on Strength and Performance
5.3 Calisthenics: Focus on Body Control and Functional Strength
5.4 Fuel and Recover for Maximum Gains
6.Mental Strategies for Success:
6.1 Mental Benefits: Stay Motivated and Avoid Burnout
7. Balanced and Strategic Progression
7.1What are the options for routines?
7.2 Routine Based on Fitness Goals
7.3 Routine Based on Split Type
7.4 Routine by Training Type
7.5 Time-Based Routines
7.6 Home vs. Gym Routines
7.7 Specialized Training Programs
7.8 Lifestyle-Specific Routines
7.9 Progressive Overload Programs
7.10 Recovery Routines
7.11 What routine suits you?
8. Injury Prevention and Joint Health
8.1 Supporting Long-Term Joint Health:
9. Customization for Individual Goals
9.1 Tailoring Your Split:
10. Mental Benefits: Stay Motivated and Avoid Burnout
How to understand your routine
It’s about to get a little “sciencey”
When you start to approach failure, your body releases hormones and builds more sarcoplasm in the muscle cell. It does this to allow itself to keep going even when you think you cant. getting those last reps are the most important part of the exercise. Whatever challenges your body the most is most likely causing the most progress as well.
Not only does intensity affect muscle growth but volume does as well. Think of it like this. If you curl 30 lbs 10 times youve curled 300 lbs in total overtime. add 5 lbs and you can only get 7 reps. the total weight was 245 lbs instead of 300. Turns out it was probably a little easier to stop at 7 reps instead of 10 depending on how long the reps take.
In some cases it’s better to hold the weight at the extended portion of the exercise where the most of the “stretch” occurs. This allows for better control in every position, more and constant muscle stimulation, and increases mechanical overload. The Mechanical tension an exercise has is important for bodybuilders to increase difficulty without increasing the weight.
When it comes to building muscle, finding the right training split is crucial.
Welcome to a revolutionary approach designed to maximize your gains and enhance your recovery like never before: The Optimized Muscle Group Split. This split focuses on hitting one muscle group per day with increased volume and intensity, while allowing for an extended recovery period. By rotating through all the major muscle groups, you ensure that each one gets the attention it needs to grow, while also giving your body the time it needs to repair and come back stronger.
Here’s why this method might be the game-changer you’ve been searching for.
Extended Rest for Maximum Recovery
One of the key advantages of this split is the extended recovery time. Traditional splits often involve working out the same muscle group multiple times a week, which can lead to overtraining and insufficient recovery. With the Optimized Muscle Group Split, each muscle group gets a minimum of 7 days of rest. This extended rest period allows for complete recovery, including the repair of muscle fibers and replenishment of glycogen stores. This recovery time is crucial for muscle growth (hypertrophy), as muscles grow during rest periods, not during workouts.
What's more important, Systematic recovery or muscle recovery?
When it comes to optimizing muscle growth, many lifters focus solely on muscle recovery—the process of repairing and growing the muscle fibers that were damaged during training. However, systemic recovery plays an equally, if not more, critical role in your overall progress.
Muscle Recovery: Repairing Local Damage
Muscle recovery refers to the localized healing of individual muscle groups after a workout. This process includes:
Protein synthesis rebuilding muscle fibers.
Reducing muscle soreness (DOMS) through nutrient replenishment.
Localized blood flow delivering oxygen and nutrients to the muscles.
While muscle recovery is crucial for hypertrophy, muscles often recover faster than the entire body does.

Systemic Recovery: The Bigger Picture
Systemic recovery goes beyond just repairing individual muscles—it ensures that your nervous system, hormones, and energy systems are fully restored. This includes:
Central Nervous System (CNS) recovery – High-intensity training can fatigue your CNS, leading to reduced strength and performance.
Hormonal balance – Intense training impacts testosterone, cortisol, and growth hormone levels. Poor systemic recovery can blunt these hormones, limiting muscle growth.
Glycogen replenishment – The body needs to restore glycogen across all muscle groups, not just the ones trained.
Joint and connective tissue recovery – Muscles may heal quickly, but tendons and ligaments require more time to fully recover.

Which One Should You Prioritize?
If muscle recovery is faster than systemic recovery, then returning to the gym too soon can lead to accumulated fatigue, overtraining, and stagnation. This is why systemic recovery is often the limiting factor in training frequency and intensity.
To optimize both:
Listen to your body: If overall fatigue is high, systemic recovery needs more attention.
Monitor sleep and stress levels: Poor sleep slows systemic recovery, even if your muscles feel fine.
Use periodization: Cycling between high and low-intensity weeks helps manage both local and global fatigue.
Balance training intensity and volume: High-intensity workouts require more systemic recovery, while higher-volume training impacts muscle recovery more.
Ultimately, systemic recovery dictates how much training your body can handle long-term. If your muscles recover but your CNS or energy systems don’t, your performance and muscle growth will suffer.
How Extended Rest Translates to Gains:
- Enhanced Muscle Repair: The muscle fibers that are torn during your workout have ample time to repair, leading to stronger and larger muscles.
- Increased Glycogen Stores: Muscles are fully replenished with glycogen, the primary fuel source for high-intensity workouts, allowing you to train harder in the next session.
- Reduced Risk of Overtraining: By allowing longer recovery periods, you avoid the pitfalls of overtraining, which can lead to fatigue, injury, and stalled progress.
Increased Volume for Superior Muscle Stimulation
This split isn’t just about rest—it’s about maximizing the work you do during each session. By focusing on one muscle group per day, you can significantly increase the volume of your workouts. This means performing more sets and reps, and incorporating a variety of exercises that target the muscle from different angles. This comprehensive approach ensures that every part of the muscle is engaged, leading to fuller development and greater overall strength.
Why Increased Volume Matters:
- Greater Muscle Fiber Recruitment: Different exercises stimulate different muscle fibers, leading to more comprehensive growth.
- Enhanced Muscle Pump: The increased volume causes more blood flow to the targeted muscle, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen for growth.
- Variety in Stimulation: By hitting the muscle from multiple angles, you ensure that all parts of the muscle are worked, leading to more balanced and aesthetically pleasing development.
Improved Intensity with Full Focus
When you only have one muscle group to focus on, you can truly dial in the intensity. With this split, you’re not conserving energy for another body part—you’re putting everything into that one muscle group. This allows you to push heavier weights, go closer to failure, and utilize advanced training techniques like supersets, drop sets, and rest-pause sets.
- Increased Strength Gains: Focusing all your energy on one muscle group allows you to lift heavier, which is key for building strength.
- Maximized Hypertrophy: Training with higher intensity and volume results in greater muscle fiber breakdown, which, when coupled with extended recovery, leads to significant muscle growth.
- Enhanced Mind-Muscle Connection: Concentrating on one muscle group improves your ability to connect mentally with the muscle, ensuring better engagement and more effective workouts.
Balanced and Strategic Progression
This split is designed for long-term progression. Because each muscle group is worked with high intensity and given plenty of time to recover, you can make steady and significant gains over time without the risk of hitting a plateau. By periodically increasing the volume, intensity, or both, you can ensure continuous improvement in muscle size and strength.
Implementing Strategic Progression:
- Periodization: Vary your training by alternating between phases of high volume/low intensity and low volume/high intensity to keep muscles responding.
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the weight you lift or the number of reps you perform to continuously challenge your muscles.
- Exercise Rotation: Every few weeks, switch out your exercises to target the muscle in new ways, preventing adaptation and promoting further growth.
How BodyBuilding, Powerlifting, and Calisthenics routines differ
Understanding the distinctions between these three training styles helps you align your workouts with your specific goals. Below is a breakdown of how bodybuilding, powerlifting, and calisthenics differ in terms of goals, training structure, and exercise selection

Bodybuilding: Focus on Aesthetics and Muscle Growth
Bodybuilding prioritizes muscle hypertrophy (size and definition). The main focus is to build and shape muscles for a balanced and aesthetic physique.
Training Structure:
- Reps and Sets: Moderate rep ranges (8-12 reps) with 3-5 sets.
- Intensity: Controlled movements with moderate to high intensity.
- Rest Periods: 30-90 seconds between sets to maintain muscle fatigue.
Exercise Selection:
- Compound movements (e.g., squats, bench press) to target large muscle groups.
- Isolation exercises (e.g., bicep curls, tricep extensions) for muscle detail.
- Machines, dumbbells, and barbells are often used.
Example Exercises:
- Dumbbell Chest Flys
- Cable Lateral Raises
- Leg Press Machine

Powerlifting: Focus on Strength and Performance
Powerlifting emphasizes maximum strength through three key lifts: the squat, bench press, and deadlift. Success is measured by lifting as much weight as possible for a single rep (1RM).
Training Structure:
- Reps and Sets: Low rep ranges (1-5 reps) with 3-6 sets.
- Intensity: Very high intensity, focusing on progressively heavier weights.
- Rest Periods: 3-5 minutes between sets for full recovery.
Exercise Selection:
- Focus on compound, full-body movements to build raw strength.
- Heavy barbell work with minimal isolation exercises.
Example Exercises:
- Barbell Back Squats
- Conventional Deadlifts
- Bench Press

Calisthenics: Focus on Body Control and Functional Strength
Calisthenics uses bodyweight exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and control. The focus is on mastering movements and achieving functional, athletic ability.
Training Structure:
- Reps and Sets: Varies based on skill level (6-15 reps for beginners, longer holds for advanced).
- Intensity: Progression comes from advancing to harder variations of exercises.
- Rest Periods: Shorter rest (30-90 seconds) to build endurance and skill.
Exercise Selection:
- Exercises that require little to no equipment.
- Progressions and regressions (e.g., push-ups → handstand push-ups).
Example Exercises:
- Pull-Ups
- Dips
- Pistol Squats
- Handstands

Fuel and Recover for Maximum Gains
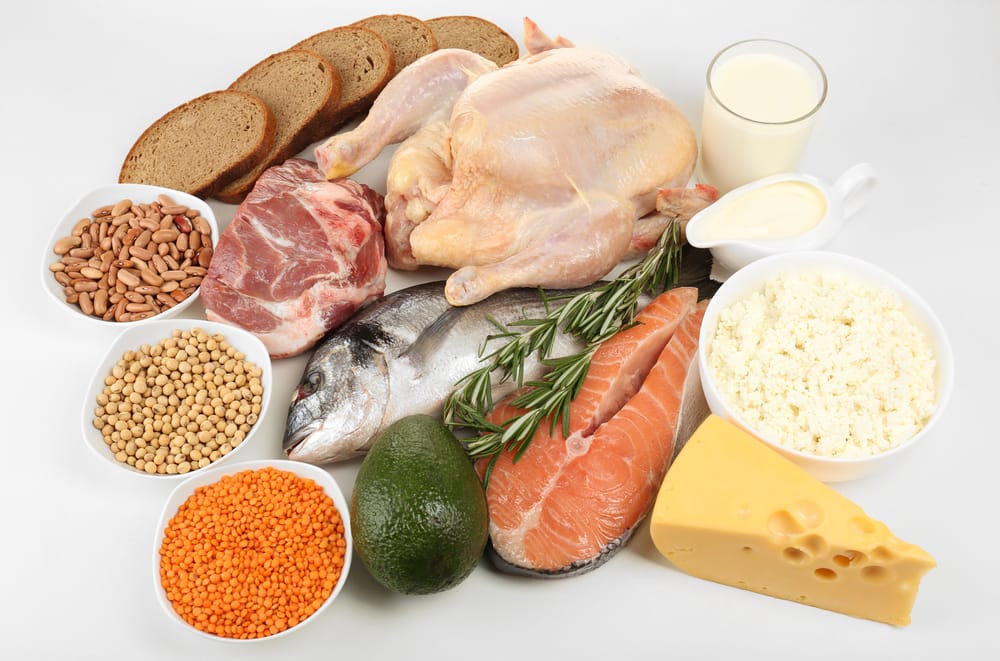
Proper nutrition is the foundation of success for bodybuilders and athletes. Without the right fuel, your body can’t recover, grow, or perform at its peak. Understanding how to balance proteins, carbs, and fats, along with key nutrients, ensures you maximize muscle growth, boost energy, and prevent injury. Simply put, training breaks your body down—nutrition builds it back stronger
Mental Strategies for Success:
Mental Benefits: Stay Motivated and Avoid Burnout
Reduced Stress and Overwhelm: Focusing on a single muscle group makes workouts feel more manageable and structured, preventing mental fatigue from trying to hit multiple areas at once
Reduced Burnout: With a balanced schedule, you avoid overtraining or feeling drained, which keeps your mindset fresh and positive for each session.
Improved Focus and Mind-Muscle Connection: By dedicating your energy to one muscle group, you can zero in on perfecting form, feeling the contraction, and truly connecting with the movements. This mindful training enhances satisfaction and progress.
Balanced and Strategic Progression
Equal Attention to All Muscle Groups: By dedicating an entire session to one muscle group, no area is neglected. This ensures balanced development and prevents overemphasis on certain muscles, leading to a more symmetrical physique.
Optimal Recovery Time: Each muscle group gets sufficient time to recover (usually 5-7 days) before being trained again, allowing for proper growth and repair without overtraining. This strategic rest enhances long-term progress.
What are the options for routines?
Routine Based on Fitness Goals
Hypertrophy (Muscle Growth):
- Focus on 6–12 reps, 3–5 sets, moderate weights, progressive overload.
- Example Split: Push-Pull-Legs (PPL), Upper-Lower, or Bro Split.
Strength Training:
- Focus on 1–5 reps, 3–8 sets, heavy weights, longer rest periods.
- Programs: 5×5, Starting Strength, Wendler 5/3/1, Texas Method.
Endurance Training:
- Light weights, 12–20+ reps, circuits, minimal rest between sets.
- Activities: High-rep weightlifting, running, rowing, cycling.
Weight Loss (Fat Loss):
- Focus on calorie burn: HIIT, circuit training, cardio + resistance combo.
- Examples: Tabata, CrossFit-style WODs, LISS cardio.
Athletic Performance:
- Explosive movements, plyometrics, agility drills, sprints.
- Programs: Sports-specific drills, Olympic lifting, agility ladder routines.
General Fitness:
- Balanced mix of cardio, strength, and flexibility exercises.
- Weekly Split: Full-body, 3–4 days/week.
Routine Based on Split Type
Full Body Workouts (3 Days/Week):
- Work every major muscle group in each session.
Upper/Lower Body Split (4 Days/Week):
- Alternate days for upper body and lower body.
Push-Pull-Legs (PPL) (3–6 Days/Week):
- Push: Chest, shoulders, triceps.
- Pull: Back, biceps.
- Legs: Quads, hamstrings, glutes, calves.
Bro Split (5–6 Days/Week):
- One muscle group per day: Chest, back, legs, arms, shoulders, abs.
Body Part Pairing Split (5 Days):
- Example: Chest + Triceps, Back + Biceps, Legs + Shoulders, Core.
Cardio + Strength Hybrid:
- Example: Mornings = Cardio; Evenings = Strength.
Routine by Training Type
Resistance Training:
- Free Weights: Dumbbells, barbells, kettlebells.
- Machines: Leg press, cable machines, etc.
- Bodyweight: Push-ups, pull-ups, squats.
Cardio Training:
- Steady-State (LISS): Walking, jogging, swimming.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Sprints, circuits.
- Low-Impact: Rowing, elliptical, cycling.
Functional Training:
- Real-life movements: Squats, lunges, deadlifts, pushing, pulling.
- Programs: TRX, kettlebell flows, farmer’s walks.
CrossFit & WODs (Workout of the Day):
- Combines strength, endurance, and HIIT.
Plyometrics (Jump Training):
- Explosive movements: Box jumps, broad jumps, clap push-ups.
Core-Focused Routines:
- Planks, sit-ups, Russian twists, hanging leg raises.
Mobility and Flexibility Routines:
- Yoga, dynamic stretching, static stretching, foam rolling.
Time-Based Routines
Short Duration (Under 30 Minutes):
Quick, intense workouts that maximize results in minimal time.
Examples:
- HIIT circuits
- Tabata training
- Bodyweight workouts
Medium Duration (30-60 Minutes):
Moderate workouts focused on building strength, endurance, and muscle.
Examples:
- Resistance training with supersets
- Cardio intervals
- Functional training circuits
Long Duration (Over 60 Minutes):
Endurance-based routines designed for sustained effort and stamina.
Examples:
- Long-distance running
- CrossFit endurance WODs
- Multi-set strength training
Time-Restricted (Timed Rounds):
Workouts designed around completing specific exercises within a set time limit.
Examples:
- AMRAP (As Many Rounds As Possible)
- EMOM (Every Minute On the Minute)
- Timed circuit training
Home vs. Gym Routines
Home Workouts:
Convenient routines that can be done in a small space with minimal equipment.
Examples:
- Bodyweight exercises: Push-ups, squats, lunges
- Resistance bands or dumbbells
- Yoga and stretching routines
Gym Workouts:
Fully equipped routines that offer a variety of machines and weights for targeted training.
Examples:
- Machine-based training: Leg press, cable machines
- Free weight exercises: Deadlifts, bench press, squats
- Group classes: Spinning, CrossFit, HIIT
Hybrid Workouts:
Combine both home and gym equipment for versatile training options.
Examples:
- Bodyweight exercises at home, weight training at the gym
- Circuit training using a mix of dumbbells, bands, and machines
- Functional training routines with minimal gear, utilizing both environments
Specialized Training Programs
Strength Training:
Focuses on building maximal strength using heavy weights and low reps.
Examples:
- Powerlifting (squat, bench press, deadlift)
- Strongman training (log press, tire flips, yoke carry)
- Olympic weightlifting (snatch, clean and jerk)
Hypertrophy Training:
Targets muscle growth with higher reps and moderate weights.
Examples:
- Bodybuilding split routines (chest, back, legs, arms)
- Isolation exercises (bicep curls, leg extensions, triceps pushdowns)
- Drop sets, supersets, and pyramid sets
Endurance Training:
Designed to improve stamina and cardiovascular endurance.
Examples:
- Long-distance running or cycling
- Swimming or rowing
- CrossFit endurance WODs
Sports-Specific Training:
Tailored to enhance performance in a particular sport.
Examples:
- Agility drills for basketball or soccer
- Sprint training for track athletes
- Plyometrics for volleyball or football
Rehabilitation Training:
Focuses on recovery and injury prevention, often prescribed by a therapist.
Examples:
- Pre-hab exercises (banded movements, mobility drills)
- Post-injury rehabilitation (physical therapy exercises)
- Low-impact workouts (swimming, elliptical, yoga)
Lifestyle-Specific Routines
Busy Schedules:
Quick, efficient workouts designed for individuals with limited time.
Examples:
- 20-minute HIIT sessions
- AMRAP (As Many Rounds As Possible) circuits
- Bodyweight workouts for home or travel
Desk Jobs & Sedentary Lifestyles:
Routines focused on improving posture, flexibility, and reducing stiffness.
Examples:
- Desk stretches (neck, shoulders, lower back)
- Standing or walking breaks
- Mobility drills and foam rolling
Active Lifestyles:
Workouts designed to complement a physically active daily routine.
Examples:
- CrossFit or endurance training
- Full-body functional workouts
- Active recovery (light cardio, stretching, yoga)
Weight Management:
Training focused on fat loss or maintaining a healthy weight.
Examples:
- Cardio intervals or steady-state cardio
- Strength training with higher reps
- Circuit training with compound movements
Pregnancy/Postpartum:
Safe and effective routines for expectant or new mothers.
Examples:
- Prenatal yoga or Pilates
- Low-impact cardio (walking, swimming)
- Postpartum pelvic floor exercises
Progressive Overload Programs
Linear Progression:
Gradually increases weight or intensity over time in a structured way.
Examples:
- Starting with a moderate weight and adding small increments each week
- Progressive rep schemes (e.g., 3 sets of 8 reps, then 3 sets of 10 reps)
- Weekly increases in sets, weight, or reps
Periodization:
Cycles different phases of training to maximize strength and muscle growth while preventing plateaus.
Examples:
- Mesocycle structure (strength phase, hypertrophy phase, endurance phase)
- Deload weeks to allow recovery and prevent overtraining
- Alternating between higher-volume and lower-volume phases
Reverse Periodization:
Focuses on building strength and power first, then shifting to hypertrophy and endurance.
Examples:
- Start with strength-focused workouts (low reps, heavy weights)
- Transition to more hypertrophy-oriented workouts (higher reps, moderate weights)
- Final phase includes endurance-based routines for conditioning
Progressive Bodyweight:
Increases the challenge of bodyweight exercises without the need for additional equipment.
Examples:
- Elevating feet for push-ups or squats
- Adding reps or sets to basic exercises (e.g., push-ups, lunges)
- Implementing advanced variations like single-leg squats, archer push-ups, or plyometric movements
Tempo-Based Progression:
Manipulates the speed of each repetition to increase time under tension and muscle growth.
Examples:
- Slowing down the eccentric (lowering) phase of lifts
- Incorporating pauses at the bottom or top of the movement
- Using fast concentric (lifting) movements with slow eccentrics
Recovery Routines
Active Recovery:
Light movement to promote blood flow and reduce soreness.
Examples:
- Low-intensity cycling or walking
- Bodyweight mobility drills
- Light resistance band exercises
Stretching & Mobility:
Enhances flexibility and prevents stiffness.
Examples:
- Dynamic stretching (leg swings, arm circles)
- Static stretching (hamstring stretch, quad stretch)
- Foam rolling and self-myofascial release
Restorative Techniques:
Methods to accelerate recovery and reduce muscle fatigue.
Examples:
- Ice baths or contrast therapy (hot/cold exposure)
- Compression therapy (sleeves, massage guns)
- Deep tissue massage and trigger point therapy
Sleep & Relaxation:
Optimizing recovery through quality rest and stress management.
Examples:
- Aiming for 7-9 hours of sleep per night
- Meditation or deep breathing exercises
- Limiting screen time before bed for better sleep quality
Nutrition & Hydration:
Fueling the body with essential nutrients for muscle repair.
Examples:
- Protein-rich meals post-workout (chicken, eggs, whey protein)
- Hydration with electrolytes to replenish lost minerals
- Anti-inflammatory foods (turmeric, berries, omega-3s)
What routine suits you?
Primary Focus: Strength, Hypertrophy & Performance
Since you’re into muscle growth, fitness, and performance, Progressive Overload Programs and Resistance Training would be ideal.
- Strength & Hypertrophy: Heavy compound lifts, short rest periods, and structured progression (e.g., 5×5, pyramid sets).
- Functional Training: To maintain agility and power for real-life movements.
- Time-Based Routines: Medium-duration (30-60 minutes) sessions for a balance of intensity and efficiency.
Complementary Training:
- Recovery Routines: Active recovery, stretching, and proper sleep will help with consistent progress.
- CrossFit & Plyometrics: If you ever want to add explosiveness, these can boost power and endurance.
- Lifestyle-Specific: If you’re busy, you might benefit from hybrid home/gym training with efficient workouts.
Injury Prevention and Joint Health
Warm-Up & Activation:
Prepares muscles and joints for movement, reducing injury risk.
Examples:
- Dynamic stretching (leg swings, arm circles)
- Light cardio (jump rope, rowing)
- Activation drills (banded glute bridges, shoulder rotations)
Joint Strengthening Exercises:
Improves stability and resilience against injuries.
Examples:
- Resistance band exercises for shoulders, knees, and hips
- Grip and forearm training for wrist support
- Balance and stability drills (single-leg stands, Bosu ball exercises)
Mobility & Flexibility:
Maintains a full range of motion and prevents stiffness.
Examples:
- Yoga and dynamic stretching routines
- Foam rolling and self-myofascial release
- Controlled Articular Rotations (CARs) for joint health
Proper Lifting & Movement Mechanics:
Ensures safe execution of exercises to prevent strain.
Examples:
- Maintaining a neutral spine during lifts
- Using proper foot positioning for squats and deadlifts
- Engaging core muscles for stability in compound movements
Recovery & Injury Management:
Aids in muscle repair and long-term joint health.
Examples:
- Ice/heat therapy for inflammation management
- Deload weeks to prevent overuse injuries
- Strengthening stabilizer muscles (rotator cuff, knee stabilizers)
Supporting Long-Term Joint Health:
- Reduced Wear and Tear: Extended rest helps prevent the repetitive strain that can lead to joint issues.
- Incorporation of Joint-Supportive Exercises: Include exercises that strengthen stabilizing muscles and improve joint health, like light resistance band work or mobility exercises.
- Smart Exercise Selection: Choose exercises that are effective yet easier on the joints, especially for those with a history of joint problems.
Customization for Individual Goals
The Optimized Muscle Group Split can be tailored to suit individual goals, whether you’re focusing on hypertrophy, strength, or a combination of both. You can adjust the volume, intensity, and exercise selection based on what you want to achieve, making this split highly versatile.
Muscle Growth (Hypertrophy):
Focuses on increasing muscle size through controlled volume and intensity.
Examples:
- Moderate to heavy weights with 8-12 reps per set
- Split routines (chest/back, legs, shoulders/arms)
- Techniques like supersets, drop sets, and time under tension
Strength & Power:
Prioritizes lifting heavier weights with lower reps for maximal strength.
Examples:
- Compound lifts (squat, bench, deadlift)
- Low-rep, high-intensity training (3-6 reps)
- Olympic lifting and explosive movements (snatch, clean & jerk)
Fat Loss & Conditioning:
Combines strength and cardio for optimal fat-burning.
Examples:
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
- Full-body circuits with minimal rest
- Strength training with short rest periods to maintain muscle
Athletic Performance:
Enhances speed, agility, endurance, and explosiveness.
Examples:
- Plyometrics (box jumps, broad jumps)
- Speed and agility drills (cone drills, sprint intervals)
- Sport-specific strength training
General Fitness & Health:
A balanced approach for overall strength, mobility, and endurance.
Examples:
- Functional training (squats, lunges, carries)
- Moderate-intensity cardio and resistance training
- Mobility work and active recovery
Rehabilitation & Injury Prevention:
Gentle, controlled movements designed to restore function.
Examples:
- Physical therapy exercises for joint stability
- Low-impact strength and flexibility routines
- Gradual progression to build back strength
Tailoring Your Split:
Full-Body Split:
Great for beginners, general fitness, or those with limited training days.
Examples:
- 2-4 training days per week
- Covers all major muscle groups each session
- Focuses on compound lifts like squats, deadlifts, presses
Upper/Lower Split:
Ideal for strength and hypertrophy while allowing muscle recovery.
Examples:
- 4 training days per week (Upper A, Lower A, Upper B, Lower B)
- Upper body (chest, back, shoulders, arms) and lower body (legs, glutes, core) split across sessions
- Can vary between strength and hypertrophy focus
Push/Pull/Legs (PPL) Split:
Common among intermediate and advanced lifters for muscle growth.
Examples:
- 3-6 training days per week
- Push (chest, shoulders, triceps), Pull (back, biceps), Legs (quads, hamstrings, glutes)
- Option to repeat for higher volume (e.g., PPL x2 per week)
Bro Split:
A traditional bodybuilding approach with a dedicated day per muscle group.
Examples:
- 5-6 training days per week
- Chest, Back, Legs, Shoulders, Arms, (optional extra day for abs or weak points)
- Maximizes muscle isolation and volume per session
Hybrid Split:
A mix of different structures to fit specific goals and recovery needs.
Examples:
- Upper/Lower + Full-Body (e.g., 3-day full-body, 2-day upper/lower)
- Strength-focused PPL with added endurance or mobility work
- Custom combinations based on weak points or lifestyle
Athletic & Functional Split:
Designed for performance, endurance, and movement efficiency.
Examples:
- Strength & Power (Olympic lifts, heavy squats)
- Speed & Agility (sprints, plyometrics, footwork drills)
- Mobility & Recovery (yoga, stretching, active recovery)
Mental Benefits: Stay Motivated and Avoid Burnout
Goal Setting & Progress Tracking:
Helps maintain focus and motivation over time.
Examples:
- Setting short-term and long-term fitness goals
- Tracking progress through workout logs or apps
- Celebrating small wins to stay motivated
Training Variety & Enjoyment:
Prevents boredom and keeps workouts engaging.
Examples:
- Mixing up training styles (strength, HIIT, functional)
- Trying new equipment or workout challenges
- Periodically changing exercises and routines
Mind-Muscle Connection & Focus:
Improves workout quality and mental clarity.
Examples:
- Practicing controlled, intentional movements
- Using visualization techniques before heavy lifts
- Training without distractions for better concentration
Stress Reduction & Mental Clarity:
Exercise can act as a natural stress reliever.
Examples:
- Releasing endorphins through physical activity
- Using workouts as a form of meditation (e.g., running, lifting)
- Incorporating breathing exercises to stay calm and focused
Balancing Intensity & Recovery:
Avoids overtraining and burnout while optimizing performance.
Examples:
- Listening to your body and adjusting workout intensity
- Scheduling deload weeks or rest days when needed
- Practicing active recovery to stay engaged without overdoing it
Discipline & Long-Term Mindset:
Builds resilience and a strong mental foundation.
Examples:
- Sticking to a routine even on low-motivation days
- Viewing fitness as a lifelong journey, not just a short-term goal
- Learning from setbacks and adapting training plans
Mental Strategies for Success:
Consistency Over Perfection:
Progress comes from showing up, not being perfect every session.
Examples:- Focus on steady improvement rather than instant results
- Stick to a routine even when motivation is low
- Understand that small setbacks don’t ruin long-term progress
Visualization & Mental Rehearsal:
Boosts confidence and performance by mentally preparing for workouts.
Examples:- Picture yourself completing a tough lift or workout before starting
- Use positive self-talk to reinforce belief in your abilities
- Mentally walk through your training plan before hitting the gym
Building a Strong Mindset:
Develops mental toughness to push through challenges.
Examples:- Train in discomfort (e.g., finish a hard set even when fatigued)
- Embrace setbacks as learning opportunities, not failures
- Stay disciplined and train even when you don’t feel like it
Accountability & External Motivation:
Keeps you on track by creating external commitments.
Examples:- Train with a partner or join a fitness community
- Use apps or journals to log progress and stay accountable
- Set deadlines for goals to maintain focus
Focus on the Process, Not Just the Outcome:
Avoids frustration by enjoying the journey of self-improvement.
Examples:- Celebrate small wins, like increasing weight or improving form
- Focus on how workouts make you feel, not just how you look
- Appreciate the benefits beyond aesthetics (strength, energy, confidence)
Overcoming Mental Fatigue & Burnout:
Prevents exhaustion and keeps training sustainable.
Examples:- Listen to your body and take deload weeks when needed
- Switch up workouts to keep things fresh and engaging
- Have non-fitness hobbies to maintain balance
Conclusion: Why the Optimized Muscle Group Split Works
An optimized muscle group split ensures efficient recovery, balanced development, and sustained progress by structuring workouts to maximize performance while minimizing fatigue. By strategically dividing training days based on muscle synergy and recovery times, this approach prevents overuse injuries, enhances strength gains, and allows for consistent progressive overload.
Key Benefits:
✔ Maximized Recovery: Each muscle group gets enough rest before being trained again.
✔ Improved Strength & Growth: Focused sessions allow for heavier lifts and higher intensity.
✔ Balanced Development: Ensures no muscle is neglected, preventing imbalances.
✔ Customizable for Any Goal: Can be tailored for hypertrophy, strength, endurance, or fat loss.
✔ Sustainability & Motivation: Prevents burnout by alternating intensity and training styles.
By following a well-structured split, you create a long-term, adaptable training system that keeps you progressing, whether you’re aiming for size, strength, or overall fitness. Stick to the plan, stay consistent, and keep adjusting based on your goals and recovery needs.
Your ideal split is the one that keeps you training hard and consistently!
Trending Articles:
Do you have any questions?